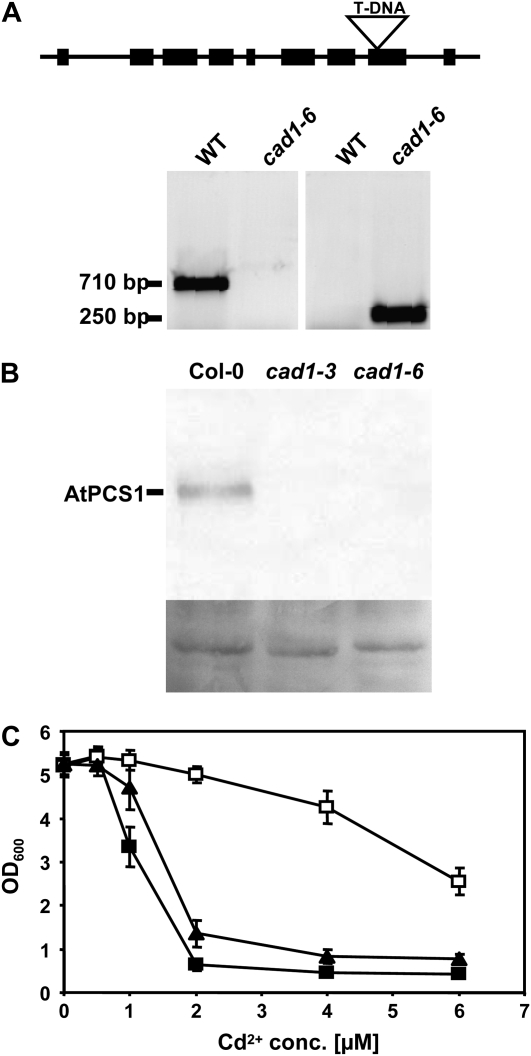
Figure 3.
Isolation of cad1-6, a homozygous T-DNA insertion mutant for AtPCS1. A, The wild-type (WT) AtPCS1 fragment of 710 bp is not detectable. Instead, a 250-bp fragment is amplified with a gene-specific primer and a T-DNA border primer (for primer sequences see “Materials and Methods”). Sequencing of this fragment confirmed the T-DNA insertion into exon 8 after bp 1229 of the coding sequence. B, Leaf extracts of Col-0, cad1-3, and cad1-6 were analyzed by SDS-PAGE, western blotting, and immunostaining with an antiserum raised against recombinant purified AtPCS1. Shown below the blot is amido black stained membrane as a loading control. C, A mutant version of AtPCS1 corresponding to the T-DNA insertion line was constructed by truncating AtPCS1 after amino acid 409. This version (AtPCS1Δ409) was expressed in the S. pombe pcsΔ mutant and growth in the presence of different Cd2+ concentrations (conc.) was compared to the mutant and the mutant expressing wild-type AtPCS1. Black squares: pcsΔ cells carrying empty vector, black triangles: AtPCS1Δ409 (cad1-6 equivalent), white squares: AtPCS1. Error bars indicate sd, n = 4.