Figure 7.
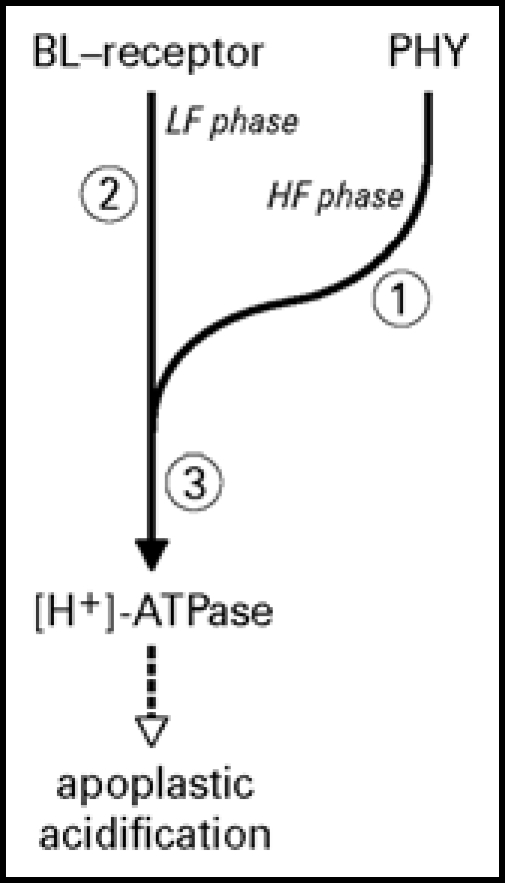
Model of the blue light signal transduction pathway of apoplastic acidification and the possible sites of ABA interaction. This model is based on the biphasic dynamic model, characterized by a high fluence (HF) component dependent on phytochrome and calmodulin, and a low fluence component (LF) independent of phytochrome and calmodulin.16 ABA can interact with the pathway at three potential sites: (1) at the phytochrome component which is dependent on calmodulin,18 (2) at the blue-light receptor-mediated pathway or (3) somewhere after the step where the two pathways are converged towards proton pump activation. By using the phytochrome deficient mutant pcd2 we have demonstrated that ABA does interact with the signaling pathway at 2 or 3. Whether ABA also affects the phytochrome-dependent pathway still remains to be determined.
