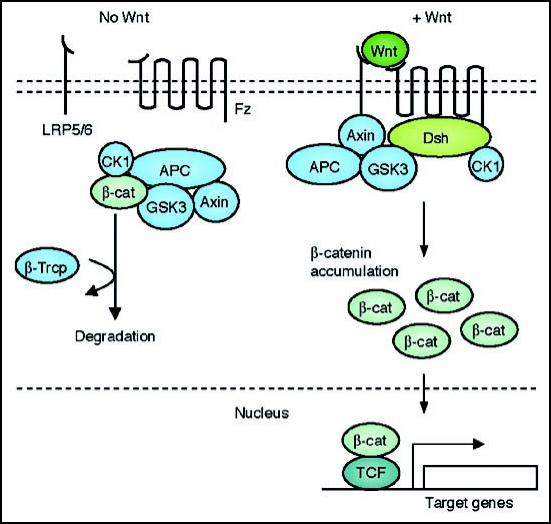
Figure 1.
A schematic representation of the canonical Wnt signal transduction cascade. Left, in the absence of Wnt ligand, a complex of Axin, APC, GSK3-β, CK1 and β-catenin is located in the cytosol. β-catenin is dually phosphorylated by CK1 and GSK3-β and targeted degraded by the proteosomal machinery mediated by β-TrCP. Right, with Wnt stimulation, signaling through the Fz receptor and LRP5/6 co-receptor complex induces the dual phosphorylation of LRP6 by CK1 and GSK3-β and this allows for the translocation of a protein complex containing Axin from the cytosol to the plasma membrane. Dsh is also recruited to the membrane and binds to Fz and Axin binds to phosphorylated LRP5/6. This complex formed at the membrane at Fz/LRP5/6 induces the stabilization of β-cat via either sequestration and/or degradation of Axin. β-catenin translocates into the nucleus where it complexes with Lef/Tcf family members to mediate transcriptional induction of target genes.