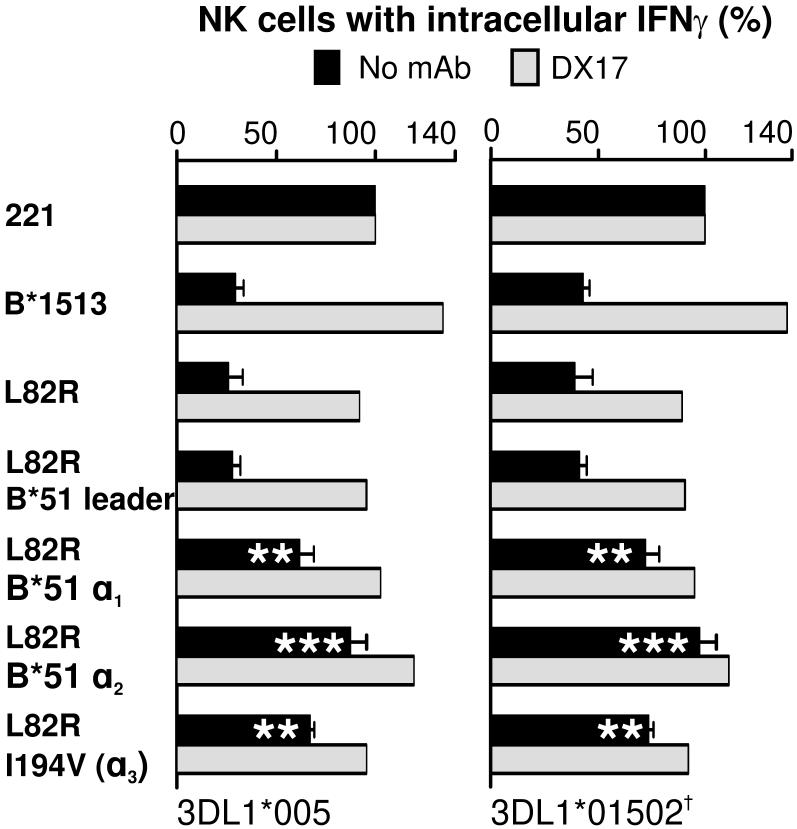
Figure 5. Polymorphisms in the α1, α2 and α3 domains contribute to the differential engagement of KIR3DL1 by B*5101-L82R and B*1513-L82R.
Further mutation of B*1513-L82R generated four mutants in which the leader peptide, the α1 domain, the α2 domain, or the α3 domain, had the B*5101 sequence. The capacity of these mutants to engage KIR3DL1*005 and *01502 on NK cells and inhibit the interferon-γ response to 221 cells was measured in the presence and absence of anti-HLA class I antibody DX17. Data shown is the average of five experiments. Statistically significant differences between mutant and wild-type are indicated by ***(p < 0.001), ** (p < 0.01), * (p < 0.05) as determined by paired t-test of means. Error bars shown are SEM. The antibody-blocking experiment was performed twice with similar results and data from one of those experiments is shown.