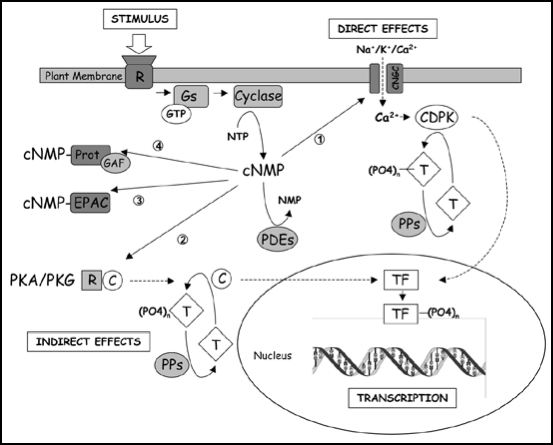
Figure 4.
Possible cyclic nucleotide transduction pathways in plants. (1) Cyclic nucleotide gated channels have been characterised in plants and are known to play important roles in pathogen response and cation transport. In addition, they can form a node in the conversion of cyclic nucleotide signals into Ca2+ based signalling which can be processed through Ca2+ sensors such as Ca2+ dependent kinases(CDPKs) and the Ca+2 signaling components CIPK-CBL. (2) Although most evidence points to its absence, it cannot be ruled out that, in analogy to mammalian cells, plants contain specific kinases that are activated by cyclic nucleotides. (3) EPACs can activate Rap-GTPases but none has been identified in plants so far. (4) Many plant proteins contain GAF domains but whether these bind and are modulated by cyclic nucleotides remains to be determined.