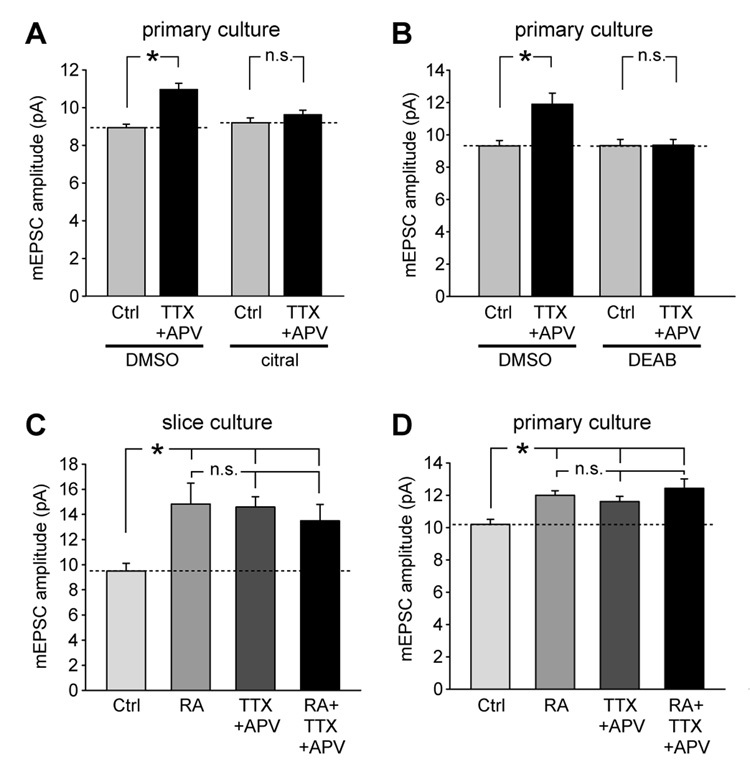
Figure 2. RA mediates activity blockade-induced synaptic scaling.
(A) Citral, a ROLDH inhibitor, blocked TTX+APV-induced synaptic scaling. Neurons were treated with citral (5 µM) or DMSO together with TTX+APV for 24 hrs before electrophysiology recording. While TTX+APV alone induced synaptic scaling (n = 10 for each group, *, p < 1 × 10−4), no synaptic scaling was induced by activity blockade (n = 9 for each group, p > 0.2). (B) DEAB (10 µM), a RALDH inhibitor, also blocked TTX+APV-induced synaptic scaling (n = 11 for each group, *, p < 0.005; n.s., p > 0.5). (C) Blocking neuronal activity in cultured slices with TTX and APV induced synaptic scaling and occluded further increase by subsequent RA treatment (n = 10/group, *, p < 0.005). (D) Activity blockade-induced synaptic scaling occluded further RA-induced scaling in primary cultures (n = 10/group; *, p < 0.01).