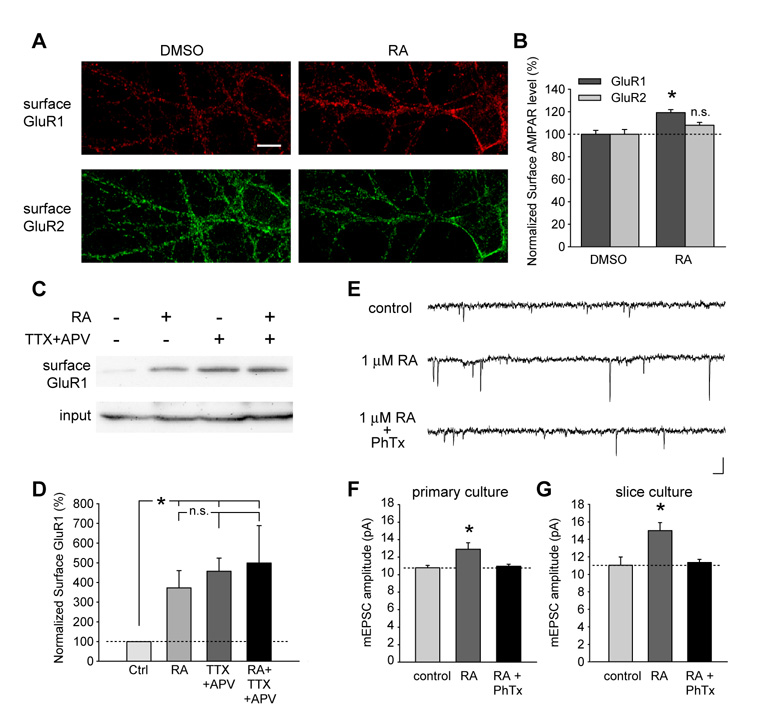
Figure 4. RA increased surface delivery of homomeric GluR1 receptors.
(A) Surface staining of GluR1 and GluR2 in neurons after 30 minutes of DMSO or RA treatment. The staining was performed an hour after drug washout. Scale bar, 10 µm. (B) RA treatment increased surface GluR1 levels without affecting GluR2 levels (n = 10 neurons/group; *, p < 0.0005). (C) Biotinylation of surface GluR1 in primary cultured neurons after 30 minutes of DMSO or RA treatment, or after 24 hours of TTX+APV treatment. (D) Both RA treatment and activity blockade increased surface GluR1 expression, but no additional increase by RA following 24-hr TTX and APV treatment was observed (n = 3; *, p < 0.01). (E) and (F) RA-induced increase in synaptic transmission is completely blocked by Philanthotoxin-433 (PhTx, 5 µM) in dissociated hippocampal cultures (n = 8; *, p < 0.05). PhTx was bath-applied 10 minutes prior to the recording. Scale bar in E: 20 pA, 20 ms. (G) RA-induced increase in mEPSC amplitude in neurons from cultured slices was also sensitive to PhTx treatment (n = 10; *, p < 0.01). Single-factor ANOVA was used for all statistical analysis. Error bars represent SEM.