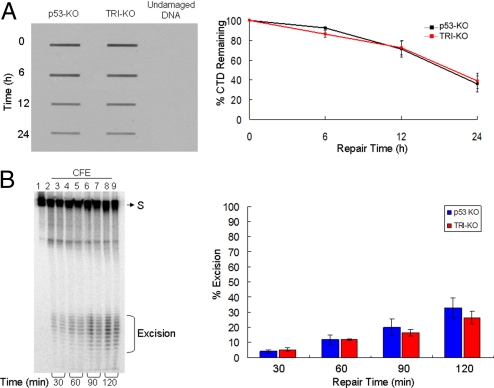
Fig. 6.
In vivo and in vitro excision repair capacity of p53-KO and TRI-KO fibroblasts. (A) In vivo repair assay. Fibroblasts of the indicated genotypes were exposed to a 10 J/m2 UV dose and the level of repair was quantified by slot-blot with anti-CTD monoclonal antibody. (Left) A representative assay. (Right) Quantitative analysis of data from 3 independent experiments including the 1 shown in Left. The repair kinetics of CTD and of (6–4) photoproducts (data not shown) of p53−/− fibroblasts are in agreement with a previous report (31). (B) (Left) Removal of (6–4) photoproducts in vitro with cell free extracts (CFE). Extracts from p53-KO and TRI-KO cell lines were incubated with a 136-bp substrate (S) containing a (6–4) T-T photoproduct, for the indicated times. Reaction products were then analyzed on a 10% sequencing gel. The excision products in the 24–32 nt range are bracketed. Lane 1, substrate without treatment; lanes 2, 4, 6, and 8, substrates treated with p53-KO fibroblast CFE for 30, 60, 90, and 120 min; lanes 3, 5, 7, and 9, substrates treated with TRI-KO CFE for 30, 60, 90, and 120 min. (Right) Quantitative analysis of the excision from 3 experiments including the 1 shown in Left. Error bars indicate standard errors of the mean. There was no statistically significant difference (P > 0.05 by a 2-sample t test) in the excision activities of the 2 extracts.