Figure 4. Both dE2F1 and dE2F2 bind to the consensus E2F binding site in the hid 5’ regulatory region.
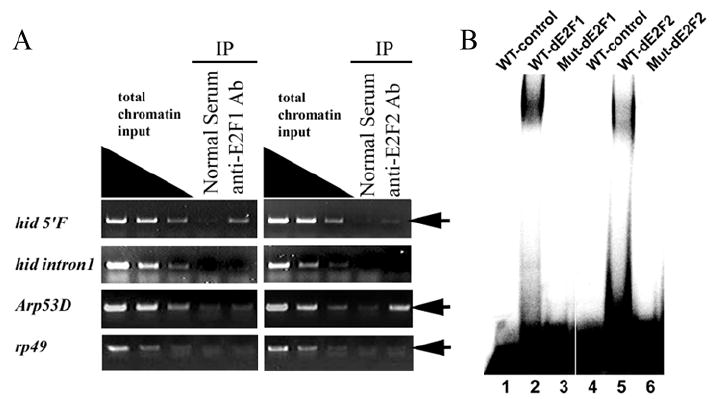
A) ChIP assay using antibodies against dE2F1 and dE2F2 proteins exhibited different degree of enrichment of the DNA fragment containing the E2F binding site at −1.4Kb in hid 5’F (first row, arrow). In contrast, ChIP with either the dE2F1 or the dE2F2 antibody failed to enrich the DNA fragment containing the introns 1 E2F site at +2.1Kb (second row). The E2F binding site in 5’ flanking sequence of Arp53D was used as a positive control for dE2F2 ChIP assay. Anti-dE2F2 highly enriched target DNA fragment (third row, arrow). rp49 was used as a negative control. No enrichment of DNA fragment was detected (fourth row, arrow). Nonspecific IgG (Normal Serum) was used as internal negative control. (B) DNA fragments containing either the WT or mutant E2F binding site of the hid 5’F locus were used as probes and recombinant dE2F1/dDP (lanes 1-3) or dE2F2/dDP (lanes 4-6) proteins were used in an EMSA assay as indicated. wild-type E2F binding site probe (WT, lanes 1, 2, 4, and 5), E2F binding site mutated probe (Mut, lanes 3 and 6).
