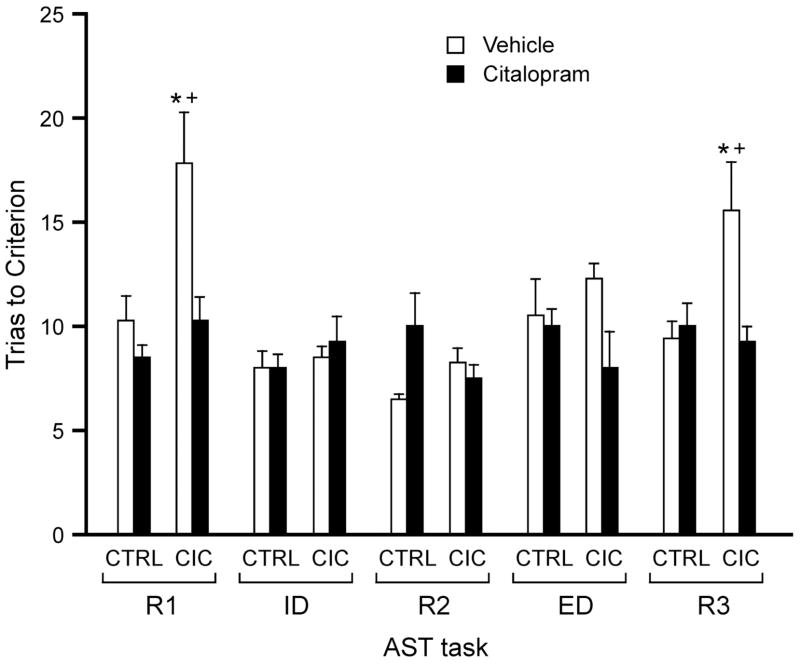
Figure 3.
Effect of acute citalopram treatment (5mg/kg, s.c.), given 30 min prior to testing on the R1 task, on the reversal deficit induced by 14-day CIC stress exposure. Only data from the R1 stage on, i.e., after drug injection, are shown. As in experiment 1, vehicle-treated CIC-stressed rats required significantly more trials to reach criterion on the R1 reversal stage compared to vehicle-treated non-stressed control rats, and also compared to CIC-stressed rats given an acute injection of citalopram. Note that in this experiment, CIC stress also induced a deficit in the third reversal task (R3), that was similarly reversed by citalopram. Citalopram-treated CIC-stressed rats did not differ from non-stressed vehicle-treated control rats on any test stage. (*p < 0.05 vehicle-treated rats, CIC-stressed compared to non-stressed controls; +p < 0.05 CIC-stressed rats, vehicle-treated compared to citalopram-treated; n = 10–11 per group).