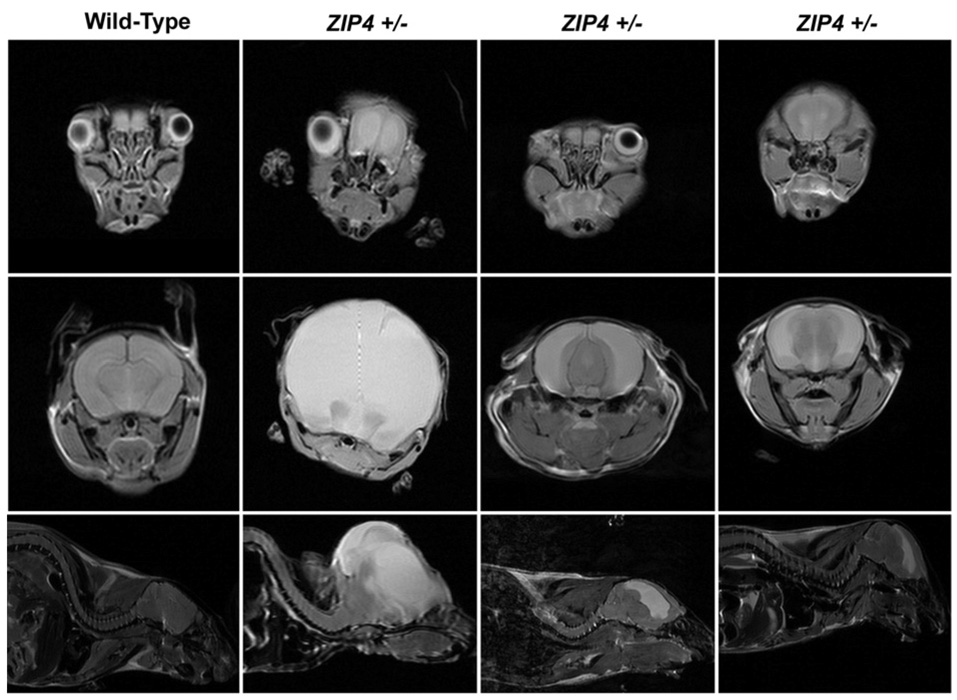
Figure 2. Zip4 haploinsufficiency is associated with abnormal development in mice.
Wild-type mice and Zip4+/−-knockout mice (Zip4+/−) that were obviously abnormal at weaning were examined using high-field MRI. Top row: axial sections through the face at the plane of the eyes. Second row: axial sections through the midbrain region. Third row: sagittal sections near the midline region. White areas in the brain indicate water accumulation. Modified from Dufner-Beattie, J., Weaver, B.P., Geiser, J., Bilgen, M., Larson, M., Xu, W. and Andrews, G.K. The mouse acrodermatitis gene Slc39a4 (ZIP4) is essential for development and heterozygosity causes hypersensitivity to zinc deficiency. Hum. Mol. Genet., 2007, vol. 16(12), pp. 1391–1399 by permission of Oxford University Press.