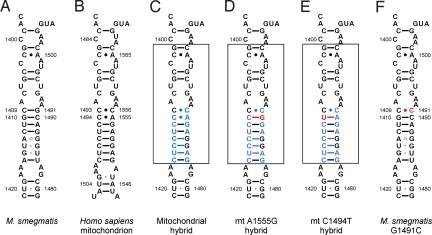
Fig. 1.
Secondary structure of rRNA helix 44 in the ribosomal decoding site. (A) Decoding site of M. smegmatis wild-type ribosomes; rRNA nucleotides are numbered according to the bacterial nomenclature (i.e., homologous E. coli 16S rRNA positions). (B) Decoding site of human mitochondrial ribosomes; rRNA residues are numbered according to the mitochondrial nomenclature. (C–E) Mitochondrial decoding sites within human-bacterial hybrid ribosomes: wild type sequence (C) and deafness-associated alterations adenine to guanine at position 1490 (corresponding to mitochondrial mutation A1555G) (D); cytosine to uracil mutation at position 1410 (corresponding to mitochondrial mutation C1494T) (E). Nucleotide positions depicted in blue represent residues that are specific for human rRNA; nucleotide positions in red highlight the pathogenic mutations; the transplanted helix is boxed. (F) Decoding site of the M. smegmatis G1491C mutant.