Figure 1.
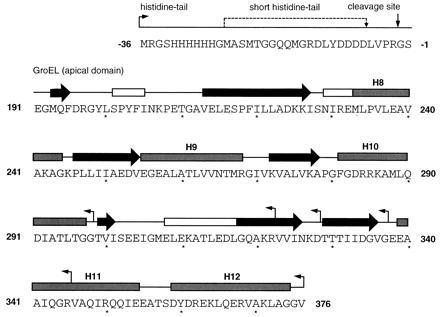
Cloning of the apical domain of GroEL and various of its fragments. The utilized expression vector coded for an N-terminal histidine-tail (ht) composed of 36 amino acids and containing a thrombin cleavage site (vertical arrow). Alternatively, a shorter version of this histidine-tail (sht) containing 17 amino acids was used. The N and C termini of the generated fusion proteins, namely ht-GroEL191-298, ht-GroEL191-322, ht-GroEL191-328, ht-GroEL191-337, ht-GroEL191-345, ht-GroEL191-376, sht-GroEL191-345, and sht-GroEL191-376 are indicated by horizontal arrows. Secondary structure is indicated by boxes and arrows for α-helix (shaded) or 310-helix (open) and β-sheet structure, respectively. Assignment of secondary structure of residues 191 to 336 was from the crystal structure of sht-GroEL191-345 using procheck (22) and the algorithm of Kabsch and Sander (23). Numbering of α-helices and secondary assignment of residues 337 to 376 according to Braig et al. (3).
