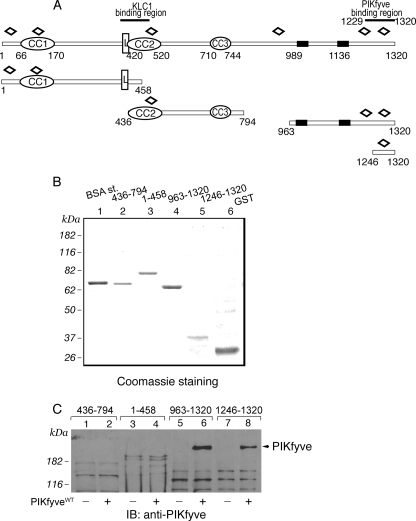
FIGURE 2.
Expression and interaction of truncated peptide fragments of GST-JLPL with PIKfyveWT by a pulldown assay. A, schematic representation of the GST-JLPL fragments used in this study. CC, coiled-coil sequences; L, leucine zipper pattern; black rectangles, putative transmembrane domains; open diamonds, tetratricopeptide repeats. B, constructs indicated in A, expressed and purified from E. coli as detailed under “Experimental Procedures,” were resolved by SDS-PAGE for qualitative and quantitative estimation versus a bovine serum albumin protein standard (BSA st;1 μg). Shown is a Coomassie Blue staining from a typical GST fusion protein production. C, indicated GST fusions (2 μg), purified and immobilized on GSH-agarose beads, were incubated (18 h at 4 °C) in the presence of cytosol isolated from HEK293 cells infected with GFP-PIKfyveWT (+) or only GFP adenovirus (-). Beads were washed with cytosol wash buffer, and captured proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE (6% gel) followed by immunoblotting as indicated. Shown is a chemiluminescence detection of a representative immunoblot (IB) of two to four independent pulldown experiments for the individual truncated forms with similar results. Some nonspecific protein absorption on the beads is seen in all lanes, but only the C-terminal JLP fragments captured specifically PIKfyve (arrowhead).