Fig. 3.
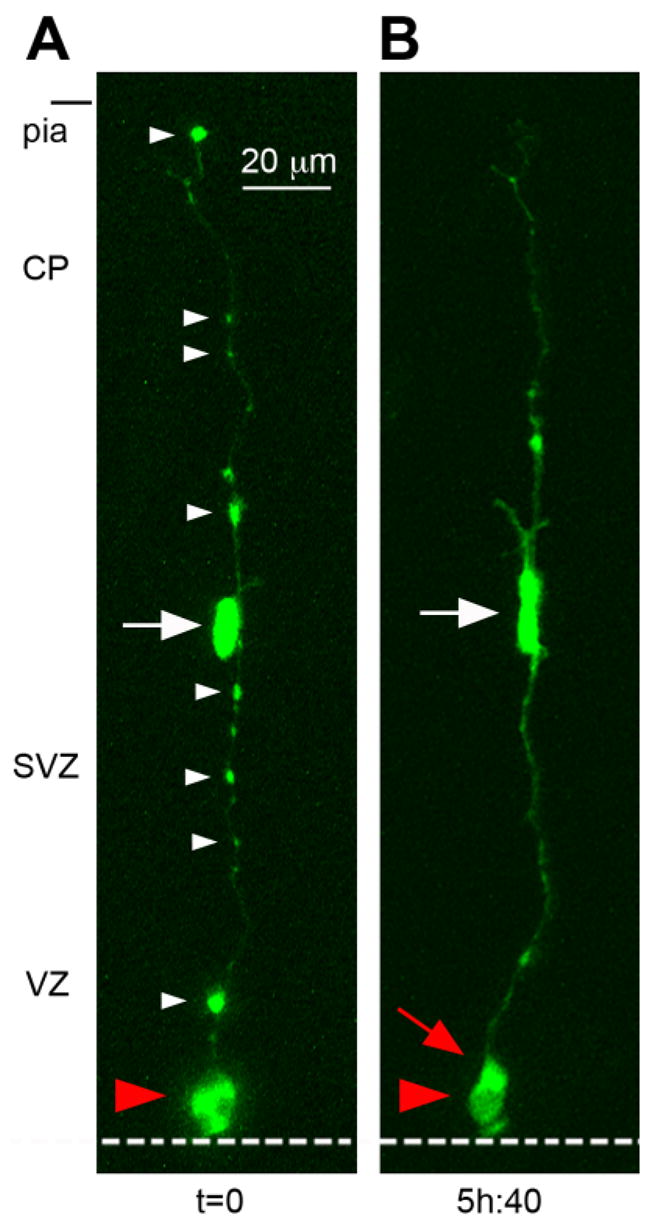
The pial fiber of mitotic radial glial (RG) cells can be identified by multiple varicosities. A: A single RG cell (red arrowhead) is shown dividing at the surface of the ventricle at t = 0. The ventricular surface is indicated by the white dotted line, the pial surface is indicated at the top of the panel. The white arrow indicates an intermediate progenitor (IP) daughter cell apposed to its parental pial fiber. The pial fiber becomes very thin during metaphase, but is identifiable by conspicuous varicosities (white arrowheads) along the entire length of the fiber. B: After division the pial fiber has become thicker, and most varicosities are no longer visible. The new RG daughter cell (red arrow) is located behind its parent RG cell in this projection image. Time is shown in hours and minutes (hh:mm) below each image. VZ, ventricular zone; SVZ, subventricular zone; CP, cortical plate. A magenta-green version of this figure can be viewed online as Supplementary Figure 3.
