Figure 2.
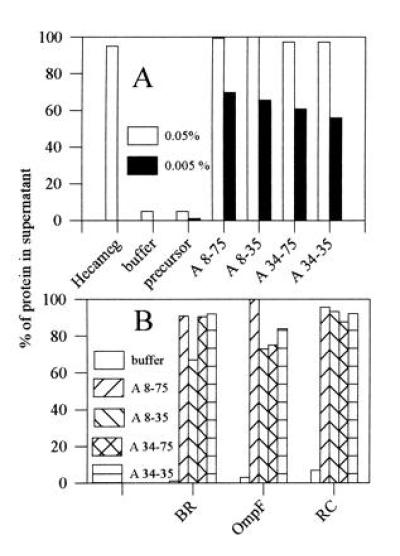
Solubility of membrane protein/amphipol complexes in aqueous solution. Aliquots from stock solutions of amphipols (5 g/liter in water) were added to purified membrane proteins in detergent solution and the mixtures diluted 10× with detergent-free buffer or with water. After 15 min incubation at 4°C, the solutions were centrifuged for 30 min at 4°C in the A-110 rotor of an Airfuge (Beckman) at 20 psi (1 psi = 6.89 kPa; ≈210,000 × g). The concentration of protein in the supernatant was determined from the absorbance at 564 nm (redox difference spectrum of b6), 546 nm (BR), 278 nm (OmpF), or 802 nm (RC). (A) Cytochrome b6f complex. Stock solution was ≈5 μM b6f complex in 20 mM HG (cmc ≈19.5 mM), 0.1 g/liter EPC, 400 mM NaOH/AP buffer (pH 8.0). Final amphipol concentrations following 10× dilution with water were 0.5 g/liter (open bars) or 0.05 g/liter (solid bars). Control experiments included dilution with a 20 mM HG solution (Hecameg) or with water (buffer) in the absence of amphipols, and dilution with water in the presence of nonderivatized low MW polyacrylate (precursor). (B) Other proteins. Stock solutions: bacteriorhodopsin, ≈0.1 g/liter in 100 mM AP (pH 8.0), ≈10% sucrose, 10 mM OTG (cmc ≈9 mM); OmpF porin, ≈4 g/liter in 0.2% (wt/wt) octyl-POE (≈9.2 mM; cmc ≈7 mM) in the same buffer; reaction center, ≈3 g/liter in 20 mM HG in 20 mM NaOH·Tricine buffer (pH 8.0). Tenfold dilution with 100 mM AP (pH 8.0) to a final amphipol concentration of 0.5 g/liter.
