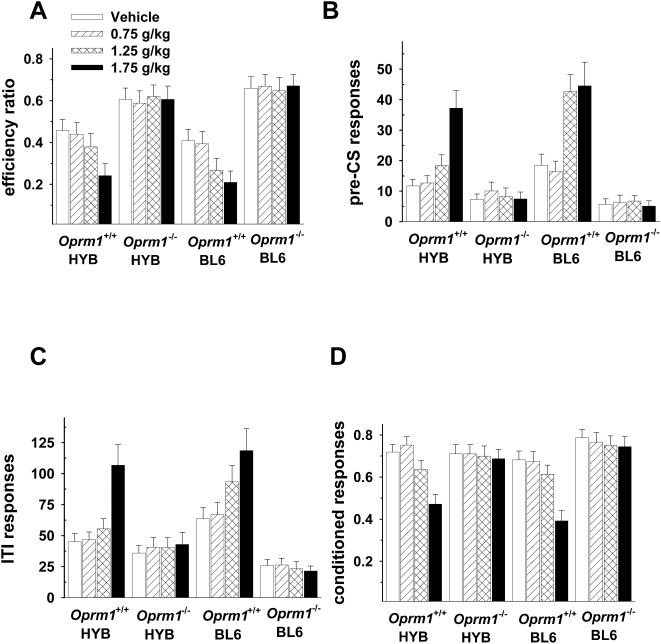
Figure 4. Oprm1 −/− mice are not affected by ethanol in the signaled nose poke task.
A: Efficiency ratios (rewards/nosepokes) decreased with increasing doses of ethanol, but only in wild-type mice. B: The same effect was observed during the pre-CS period. There were no significant strain differences on any behavioral measure during ethanol testing, nor were there any strain-dose interactions. C: Ethanol increased nose pokes that occurred during the inter-trial interval (ITI) in wild-type but not knockout animals. D: Ethanol also altered conditioned responses in Oprm1 +/+ , but not Oprm1 −/− mice. The highest dose of ethanol (1.75 g/kg) produced the greatest effect on conditioned responses in wild-type mice. Oprm1 +/+ HYB, n = 11; Oprm1 +/+ BL6, n = 12; Oprm1 −/− HYB, n = 10; Oprm1 −/− BL6, n = 11.