Figure 2.
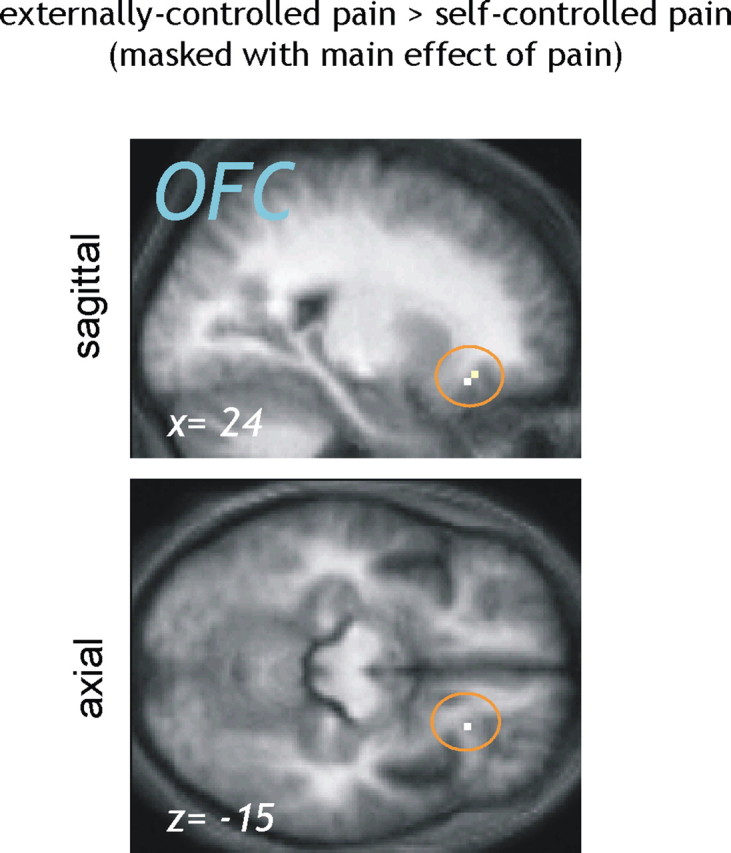
Brain responses to externally controlled compared with self-controlled pain (masked with main effect of pain). To identify pain-related brain regions that were less active when the painful stimulation was perceived as controllable, the contrast “externally > self-controlled pain” (p < 0.001 uncorrected) was masked by the main effect of pain (p < 0.001 uncorrected). A significant reduction in pain-related activity under perceived control was observed in the right lateral OFC [peak voxel, coordinates of (24, 27, −15)].
