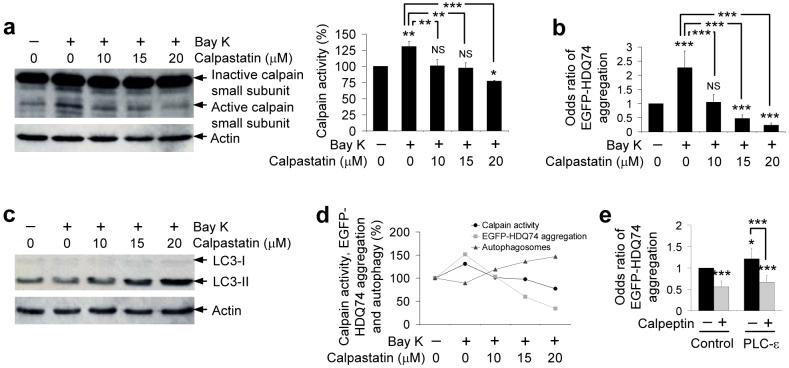
Figure 3. The effects of L-type Ca2+ channel agonist on autophagy and mutant huntingtin aggregation are abrogated by calpain inhibition.
a, SK-N-SH cells were pre-treated with or without 10, 15 or 20 μM calpastatin for 15 min followed by addition of 1 μM (±)-Bay K8644 for 4 h. Calpain activity was detected by immunoblotting with anti-calpain small subunit antibody. Densitometry analysis is relative to actin. Error bars: Standard error of mean.
b, SK-N-SH cells transfected with EGFP-HDQ74 for 4 h, then pre-treated with or without 10, 15 or 20 μM calpastatin for 15 min followed by addition of 1 μM (±)-Bay K8644 for 48 h post-transfection, were assessed for the proportion of EGFP-positive cells with EGFP-HDQ74 aggregates. Error bars: 95% confidence interval.
c, SK-N-SH cells were pre-treated with or without 10, 15 or 20 μM calpastatin for 15 min followed by addition of 1 μM (±)-Bay K8644 for 4 h. Endogenous LC3-II levels were detected by immunoblotting with anti-LC3 antibody.
d, Comparison between calpain activity, EGFP-HDQ74 aggregation and autophagosomes as seen in Fig. 3a-c. The control condition for all the assessments was set at 100%. Calpastatin lowered the increased calpain activity and EGFP-HDQ74 aggregation caused by (±)-Bay K8644 in a dose-dependent manner with a simultaneous increase in LC3-II levels (autophagosomes).
e, COS-7 cells transfected with empty vector (pcDNA3.1) or wild-type PLC-ε for 4 h and treated with or without 50 μM calpeptin for 48 h post-transfection were assessed for the proportion of EGFP-positive cells with EGFP-HDQ74 aggregates. Error bars: 95% confidence interval. ***, p<0.001; **, p<0.01; *, p<0.05; NS, Non-significant.