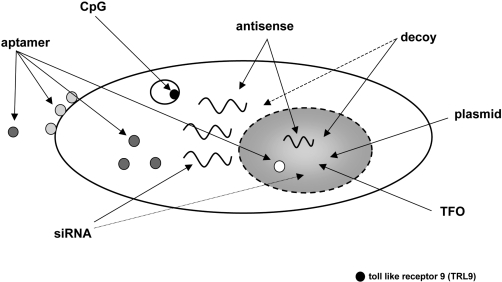
Figure 1.
Cellular target sites of oligonucleotides with therapeutic potential. Aptamers, small oligonucleotides derived from an in vitro evolution process called SELEX, can virtually be targeted to any given extra- or intracellular structure. Oligonucleotides containing a CpG motif interact with toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) and trigger an immunostimulatory response. Antisense and decoy oligonucleotides as well as siRNAs can modulate gene expression by interacting with RNA or proteins either in the cytoplasm or in the nucleus. TFOs are directed against genomic DNA and, like plasmids, have to reach the nucleus to exert their biological effect.