Figure 2.
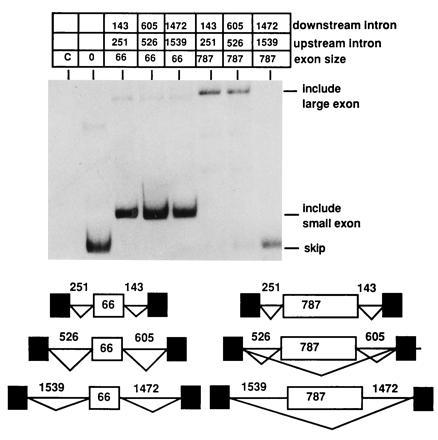
Expanding small introns flanking a large exon causes exon skipping. The MT constructs shown in Fig. 1C containing either the natural 66-nt second exon from MT or the 787-nt internally expanded second exon were altered to increase the lengths of both introns. Intron lengths in the final constructs are indicated. RNA splicing phenotypes were determined by RT-PCR as described in Fig. 1 using radiolabeled PCR primers. Products resulting from skipping of the middle exon or inclusion of either the small or large internal exon are indicated.
