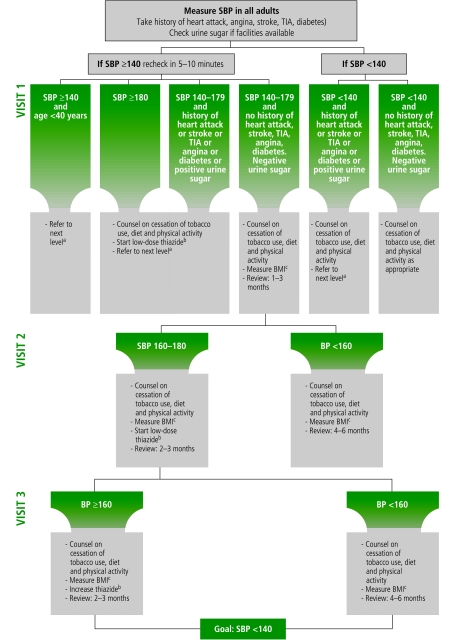
Fig. 1.
Patient management algorithm in Scenario I: WHO CVD-Risk Management Package
CVD, cardiovascular disease; BMI, body mass index; BP, blood pressure; SBP, systolic blood pressure, TIA, transient ischaemic attack.
a In areas where coronary artery diseases rates exceed stroke rates.
b Thiazide diuretic: Hydrochlorothiazide starting dose 12.5 mg (low-dose) to be increased up to 25 mg (maximum dose).
c Second drug option: use the cheapest out of beta-blockers or calcium-channel blockers or ACE-inhibitors.
If drugs given in footnotes (b) and (c) are not available: use methyldopa or reserpine or fixed dose combination.
Source: WHO CVD-Risk Management Package for low- and medium-resource settings.