Figure 7. hDNA2 deficiency affects the efficiency of repairing oxidative DNA damage in mitochondria.
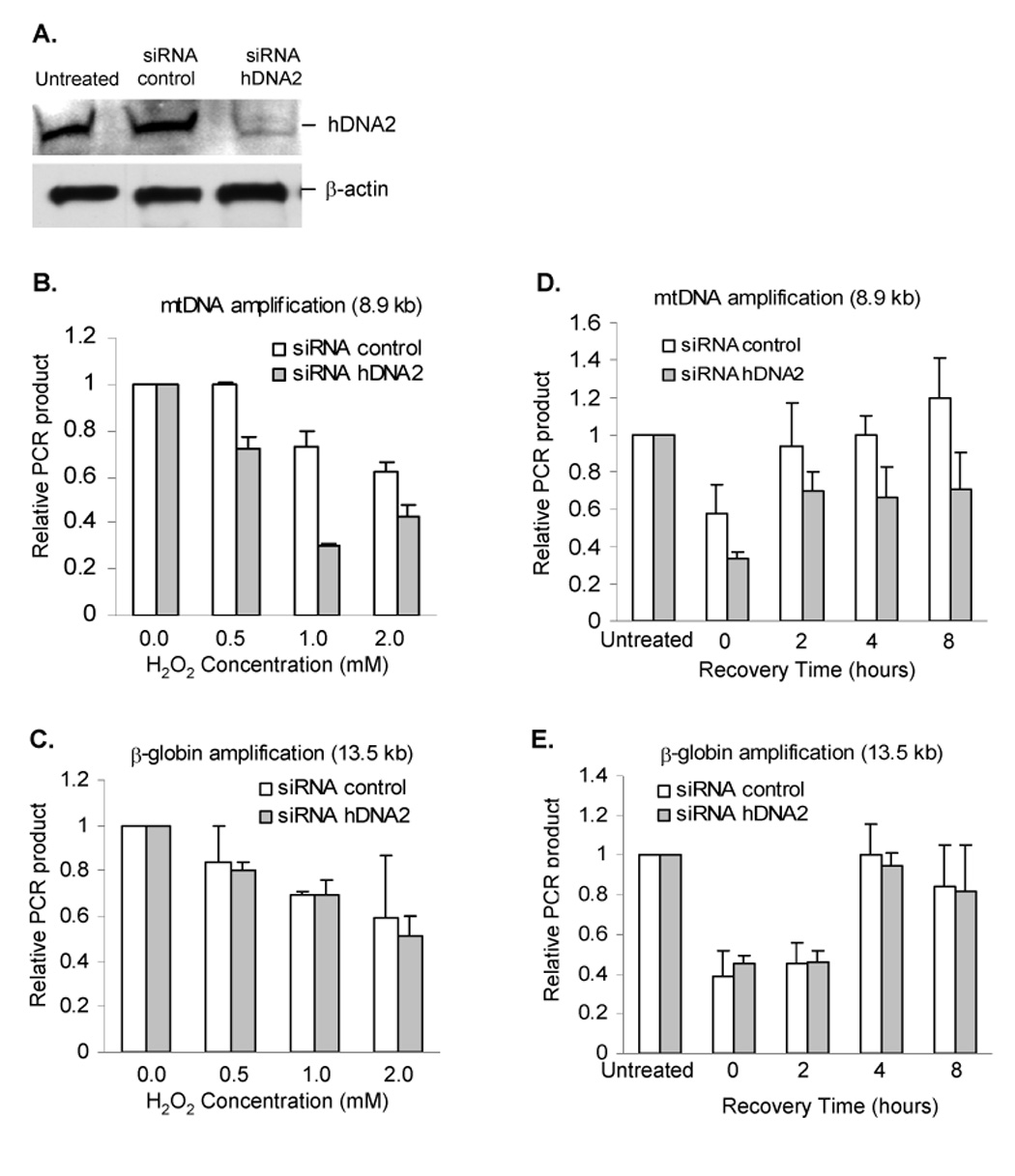
A. SiRNA knockdown of hDNA2. Knockdown efficiency was determined by Western blotting analysis of whole cell extract from HeLa cells not treated with RNA oligos (Lane 1, untreated) or transfected with control siRNA oligos (Lane 2, siRNA control) or siRNA specific to hDNA2 (Lane 3, siRNA-hDNA2). B. and C. H2O2-induced oxidative DNA damage in mitochondria (B) nuclei (C). A long-range QPCR protocol was used to evaluate the oxidative damage in mtDNA or nuclear DNA as induced by H2O2 treatment. The relative PCR amplification of 8.9 kb mtDNA fragment or 13.5 kb nuclear DNA fragment was normalized to mtDNA copy number or total amount of nuclear DNA. D. and E. Time-course of recovery from H2O2 treatment. HeLa cells were treated with 2 mM H2O2 and allowed 0, 2, 4, or 8 h to repair the damage before harvesting for DNA isolation and QPCR analysis of oxidative damage in mtDNA (D) and nuclear DNA (E). All values were mean ± SD (n=3).
