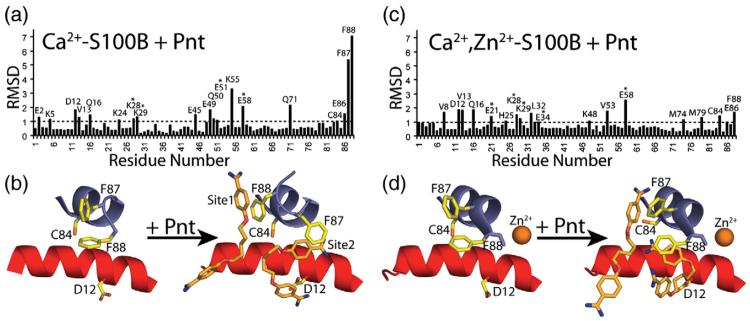
Fig. 7.
Changes in side-chain positioning upon the binding of Pnt to Ca2+–S100B or to Zn2+,Ca2+–S100B. (a) Average RMSDs for the position of side-chain atoms when the X-ray structures of Ca2+–S100B and Pnt–Ca2+–S100B are compared. Those residues that have an average RMSD value greater than 1 are labeled, and residues marked with an asterisk (*) are involved with the crystallographic lattice. (b) Residues on helix 4 (blue) and helix 1′ (red) of Ca2+–S100B in the absence and presence of Pnt (orange) illustrating the change in side-chain positioning upon drug binding. (c) Average RMSDs for the position of side-chain atoms when the X-ray structures of Zn2+,Ca2+–S100B and Pnt–Zn2+,Ca2+–S100B are compared. Those residues that have an average RMSD value greater than 1 are labeled, and residues marked with an asterisk (*) are involved with the crystallographic lattice. (d) Residues on helix 4 (blue) and helix 1′ (red) of Zn2+,Ca2+–S100B in the absence and presence of Pnt (orange) illustrating the change in side-chain positioning upon drug binding.