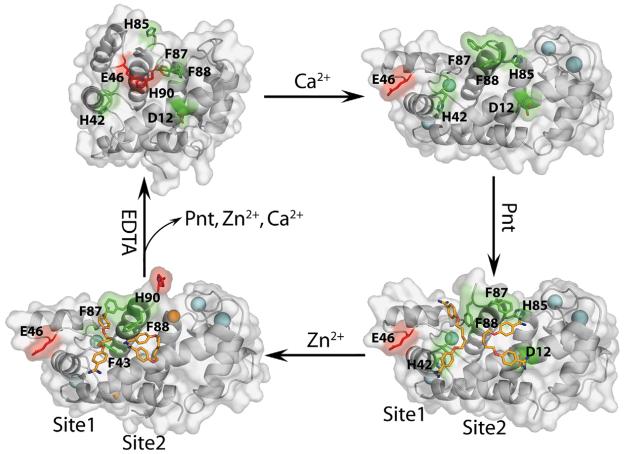
Fig. 9.
The calcium dependence of Pnt binding to S100B. Shown are ribbon/surface diagrams of apo–S100B (NMR, PDB code: 1B4C; top left), Ca2+–S100B (X-ray, PDB code: 1MHO; top right), Pnt–Ca2+–S100B (X-ray, PDB code: 3CR4; bottom right), and Pnt–Zn2+,Ca2+–S100B (X-ray, PDB code: 3CR5; bottom left). A hydrogen bond between His90 and Glu46 (red) that occludes both Pnt binding sites (residues in sites 1 and 2 are colored green) is observed in apo–S100B (top left). Upon binding Ca2+ (top right), helix 3 reorients (see Fig. 1) and Glu46 is rotated out to the surface of the protein and His90 becomes dynamic and unobservable. Residues involved in Pnt binding two sites on S100B (highlighted in green) start to become localized as necessary for formation of the Pnt–Ca2+–S100B complex (lower right). Upon binding Zn2+,a second conformational change occurs, and surprisingly, Pnt is still able to bind both sites 1 and 2 (see also Figs. 6 and 7).