Figure 10.
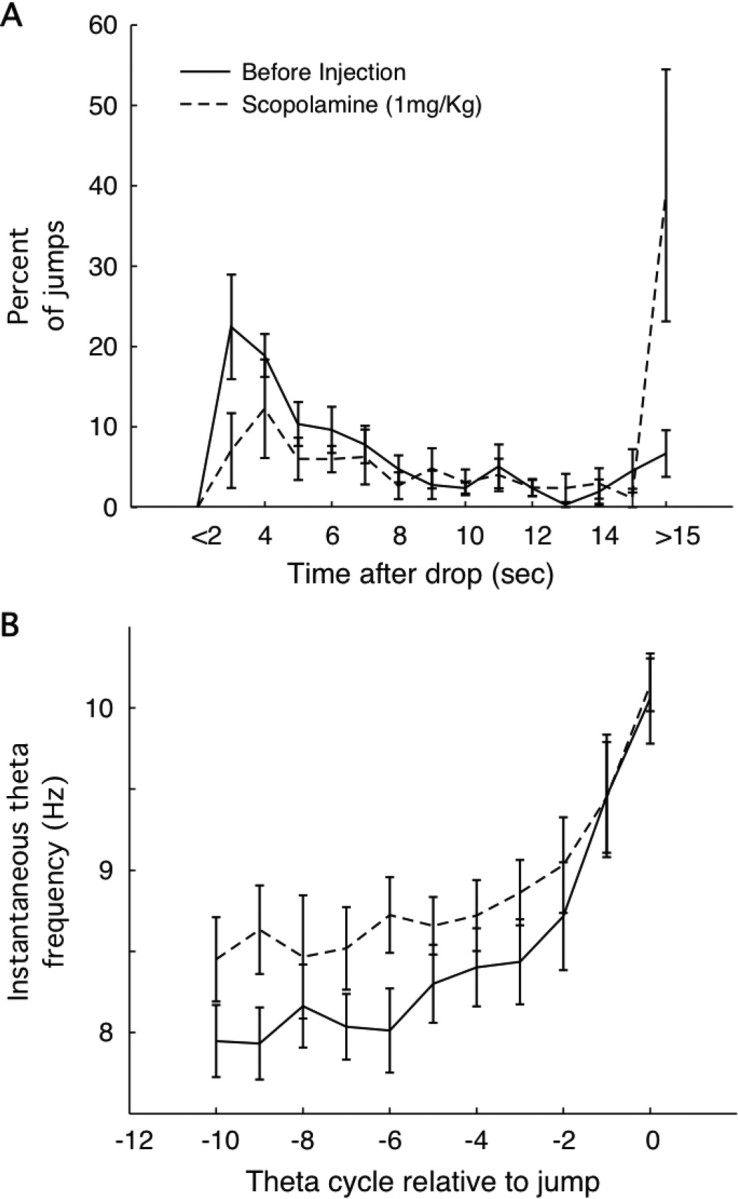
Effects of 1.0 mg/kg scopolamine on jumping behavior and theta frequency activity in the hippocampal EEG. A, Averaged over rats, the fraction of successful avoidances (jump time <15 s after drop) increases from ∼5 to ∼40%. For successful jumps, the post-scopolamine relationship between percentage and time after drop looks like a scaled-down version of the relationship before scopolamine. B, For successful jumps, the instantaneous theta band frequency increases as jump time approaches to reach ∼10.5 Hz. Interestingly, the frequency is higher at earlier times (∼1.0 s before jump).
