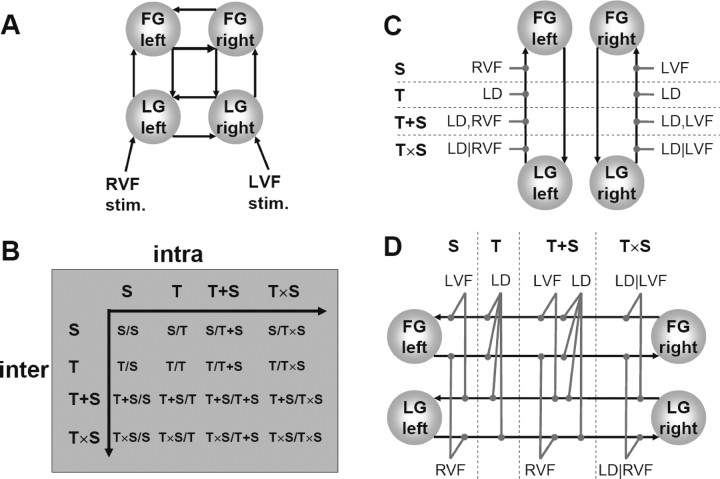
Figure 2.
A, Basic structure of the four-area ventral stream model, comprising the reciprocally connected LG and FG in both hemispheres. Because of the nonfoveal stimulus presentation, stimuli in RVF and LVF drive contralateral LG activity. During the instruction periods, bilateral visual field input was provided for 6 s; this was modeled as a boxcar input affecting LG in both hemispheres (not shown here). The basic four-area model for the dorsal stream, comprising cuneus and superior parietal gyrus in both hemispheres, was constructed in an analogous manner (see Materials and Methods and Fig. 6). B–D, Schema of how 16 variants of the ventral stream model (B) were constructed by systematically combining four different types of modulatory inputs for intrahemispheric (C) and interhemispheric (D) connections. The strength of a connection could depend (1) only on the visual field of stimulus presentation (the S model, for stimulus-dependent), (2) only on whether a specific task is performed or not (T model, for task-dependent), (3) on both the task and the visual field, but independently of each other (the T+S model), or (4) on both the task and the visual field, but in a conditional manner [i.e., the connection strength is only modulated by task if the stimulus was presented in a particular visual field (the T×S model)]. These possibilities equally exist for interhemispheric and the intrahemispheric connections. However, we initially constrained the combinations by only allowing for modulation of the forward intrahemispheric connections. This constraint was subsequently evaluated in additional models and found to be appropriate (see Results). Overall, this combinatorial approach resulted in 64 different DCMs per subject (16 DCMs each for the four-area and six-area models of both the ventral and dorsal stream). Models are generally referred to by first listing the modulation of interhemispheric connections, followed by the modulation of intrahemispheric connections (B). Analogous model variants were constructed for the dorsal stream, using SD as task.