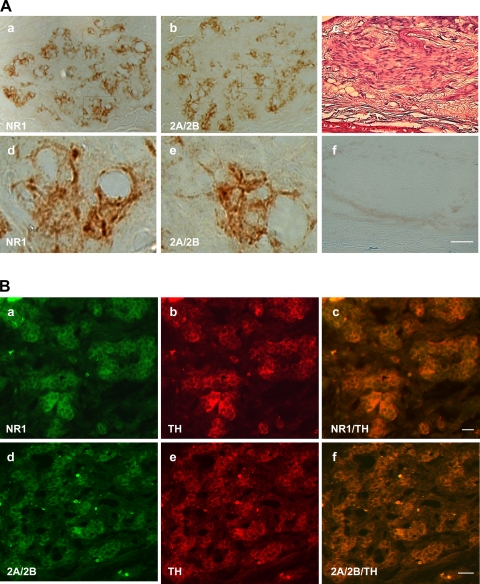
Fig. 2.
A: immunohistochemical reactive staining for NMDAR1 (a) and NMDAR2A/2B (b) revealed products of these receptors in carotid body; d and e are higher magnifications of framed areas in a and b, respectively. c: Hematoxylin and eosin staining to show carotid body. f: Negative staining control obtained by omitting the primary antibody in a consecutive section adjoining c. Scale bar (applies to all images) = 20 μm. B: additional immunofluorescent staining further revealed NMDAR1 (a–c) and NMDAR2A/2B (d–f) in clusters of glomus cells in rat carotid body. Stain for tyrosine hydroxylase (b and e) confirmed the identification of glomus cells. Double staining for tyrosine hydroxylase and NMDAR1 (c) or NMDAR2A/2B (f) confirmed colocalization of the NMDA receptors and tyrosine hydroxylase in glomus cells. Scale bars = 20 μm.