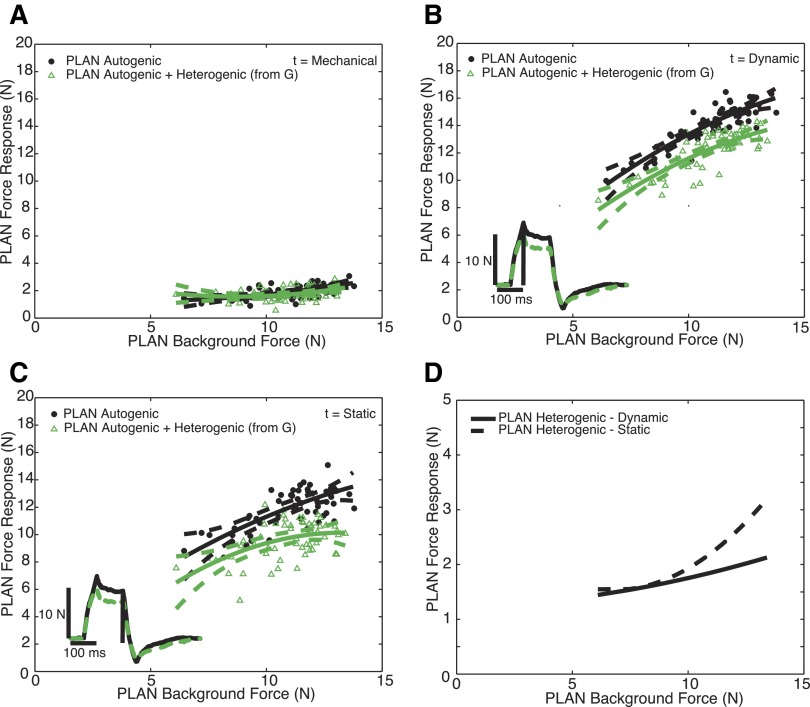
FIG. 6.
Heterogenic inhibition from G onto plantaris muscle (PLAN), where G is the donor muscle and PLAN is the recipient muscle in 1 animal during locomotion with force oscillations for the mechanical phase (A). B: heterogenic inhibition from G onto PLAN during locomotion for the dynamic phase. C: heterogenic inhibition from G onto PLAN during locomotion for the static phase. The same conventions as Fig. 5 apply. Two traces matched at 10 N background force in PLAN from R (—) and RD (- - -) have been superimposed to illustrate the magnitude of inhibition from G onto PLAN during locomotion, and the vertical line indicates the sample time. Heterogenic inhibition from G onto PLAN during locomotion remains independent of force during the dynamic phase yet increases with increasing force during the static phase. Variability also increases with increasing time. The magnitude of heterogenic inhibition onto PLAN for the dynamic and static time points (D) are represented as the difference between polynomials depicted in B and C.