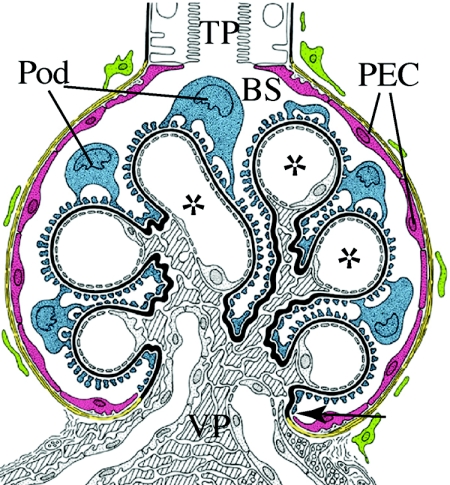
Figure 1.
Renal glomerulus. The glomerular epithelium consists of PECs (red) and podocytes (Pod; blue), which reside on the capillary convolute. Both epithelia adjoin directly at the vascular pole (VP; arrow). At the tubular pole (TP), the parietal epithelium is connected to the epithelium of the proximal tubule. In male mice, this transition from PECs to proximal tubular cells often occurs within the glomerulus. The glomerular basement membrane (black) forms a continuous barrier between the glomerular epithelium and the endocapillary compartment that contains mesangial cells (shaded) and endothelial cells of the glomerular capillaries (*). Primary urine is filtered across the three-layered filtration barrier (endothelial cells, glomerular basement membrane, and Pod) into Bowman's space (BS).