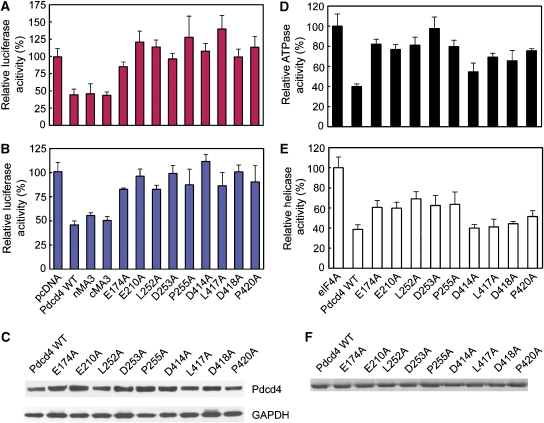
Figure 4.
Functional analysis of the Pdcd4–eIF4A interaction. (A) In vivo translational inhibition by wild-type (WT) and mutants Pdcd4 proteins. The luciferase activity in the absence of Pdcd4 is designated as 100%. The mean values and s.d. from three independent experiments are shown. (B) Inhibition of in vivo AP-1 dependent transcription by WT Pdcd4 and its variants measured by the relative luciferase activity. The mean values and s.d. from three independent experiments are shown. (C) Similar expression levels of wild-type and mutant Pdcd4. RT101 cell lysates (10 μg) from transient transfection with wild-type Pdcd4 and Pdcd4 mutant expression plasmids were separated on 4–20% Bis–Tris NuPage gels, transferred to nitrocellulose, and subjected to immunoblotting with Pdcd4 antibody, with visualization by chemiluminescent detection. (D) Defective eIF4A-binding mutants of Pdcd4 are unable to inhibit the ATP hydrolysis activity of eIF4A, depicted as percentage of eIF4A ATPase activity in the absence of Pdcd4 (mean values of three independent experiments±s.d.). (E) Inhibition of eIF4A RNA helicase activity by WT Pdcd4 and its mutants depicted as percentage of eIF4A helicase activity in the absence of Pdcd4. (mean values of three independent experiments±s.d.). (F) Similar protein expression levels of WT and mutant Pdcd4. Purified proteins were separated on 12% SDS–PAGE gels and stained with Coomassie blue.