FIGURE 6. Id1 expression inhibits Ig gene diversification and λR/E2A colocalizations.
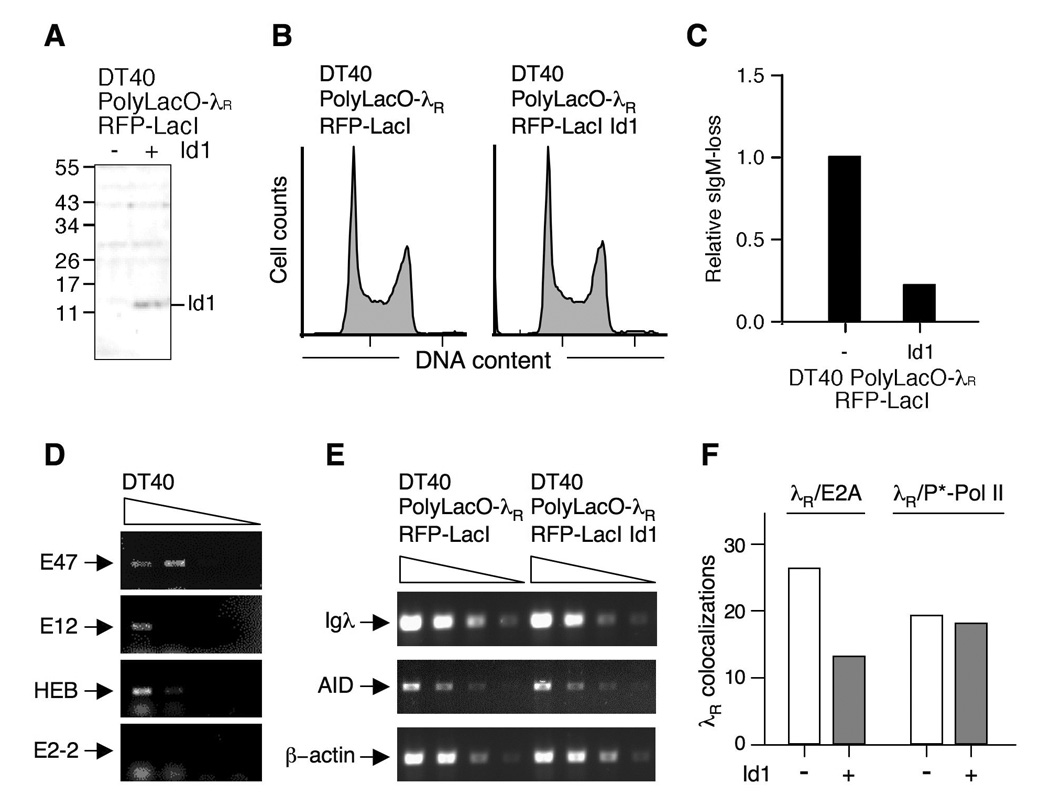
A. Western blot assaying Id1 expression in DT40 PolyLacO-λR RFP-LacI (left) and DT40 PolyLacO-λR RFP-LacI Id1 cells (right). Marker polypeptide sizes (kDa) at left.
B. Cell cycle profile of DT40 PolyLacO-λR RFP-LacI and DT40 PolyLacO-λR RFP-LacI Id1 cells.
C. Mean sIgM-loss of independent clonal DT40 PolyLacO-λR RFP-LacI Id1 transfectants (n = 6), cultured for 6 wk. Values were normalized to DT40 PolyLacO-λR RFP-LacI cells.
D. RT-PCR analysis of mRNA expression of E proteins in DT40 cells. Arrows indicate predicted sizes of products; smudge below (HEB, E2-2) is due to unincorporated primers.
E. Id1 expression does not alter Igλ or AID transcript levels. RT-PCR analysis of expression of Igλ, AID or β-actin control mRNA in DT40 PolyLacO-λR RFP-LacI and DT40 PolyLacO-λR RFP-LacI Id1 cells.
F. Id1 expression diminishes λR/E2A colocalizations. Colocalizations of λR/E2A and λR/P*-Pol II in asynchronous populations of DT40 PolyLacO-λR RFP-LacI cells and a derivative stably expressing Id1 (Id1 − and +, respectively).
