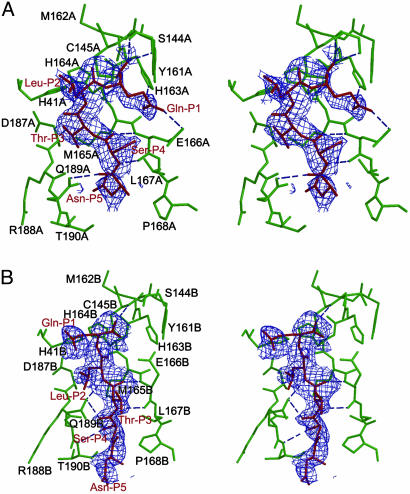
Fig. 4.
Molecular recognition interactions in the substrate-analogue hexapetidyl CMK inhibitor (Cbz-Val-Asn-Ser-Thr-Leu-Gln-CMK) complexed with SARS Mpro. (A) A stereoview of the substrate-binding pocket (green) in protomer A of the CMK inhibitor complex. The inhibitor molecule (red) is shown in the 2.5-Å original Fo - Fc difference electron-density map (1.5 σ). Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. The Gln-P1 is bound to the S1 substrate-specificity subsite, but Leu-P2 fails to bind at the S2 subsite (near Asp-A187), which is instead occupied by Thr-P3. The amino acid residues of the protein are labeled in single letters; for example, H163A stands for His-163 of monomer A (i.e., His-A163). (B) A stereoview of the substrate-binding pocket (green) in protomer B of the CMK inhibitor complex. The inhibitor molecule (red) is shown in the original Fo - Fc difference electron-density map (1.5 σ). The Gln-P1 does not bind to the partly collapsed S1 subsite in this protomer, but Leu-P2 and Ser-P4 are in their canonical binding sites. See text for further details.