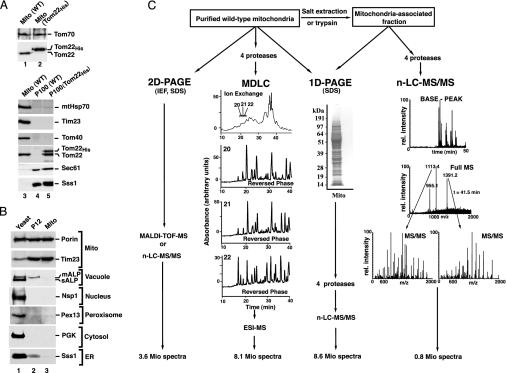
Fig. 1.
Purification of yeast mitochondria, separation of proteins, and analysis by MS. (A) Subcellular localization of authentic and tagged Tom22. Mitochondria (Mito; 25 μg of protein) and enriched microsomal fractions (25 μg of protein; P100) from WT and Tom22His-10 S. cerevisiae strains were separated by SDS/PAGE and transferred onto poly(vinylidene difluoride) membranes. Immunodecoration was performed with antisera against the indicated proteins and the ECL detection system (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech). Sec61 and Sss1 are subunits of the ER translocon. (B) Highly purified yeast mitochondria. Equal-volume aliquots from total yeast, P12, and highly purified mitochondria were separated by SDS/PAGE and blotted onto poly(vinylidene difluoride) membranes. mALP, mature vacuolar alkaline phosphatase; sALP, soluble vacuolar alkaline phosphatase; Nsp1, subunit of nuclear pore complex; Pex13, peroxisomal biogenesis protein (peroxin) 13; PGK, phosphoglycerate kinase 1. (C) Strategies for protein separation and MS analysis. Four separation methods were used to cover the mitochondrial proteins: isoelectric focusing (IEF) followed by SDS/PAGE (2D PAGE); digestion with four different proteases, followed by multidimensional liquid chromatography (MDLC) and electrospray ionization-MS (ESI-MS); 1D SDS/PAGE, followed by n-LC-MS/MS; generation of a mitochondria-associated fraction by treatment of mitochondria with trypsin or salt, followed by SDS/PAGE and n-LC-MS/MS. Typical examples of separation and spectra are shown.