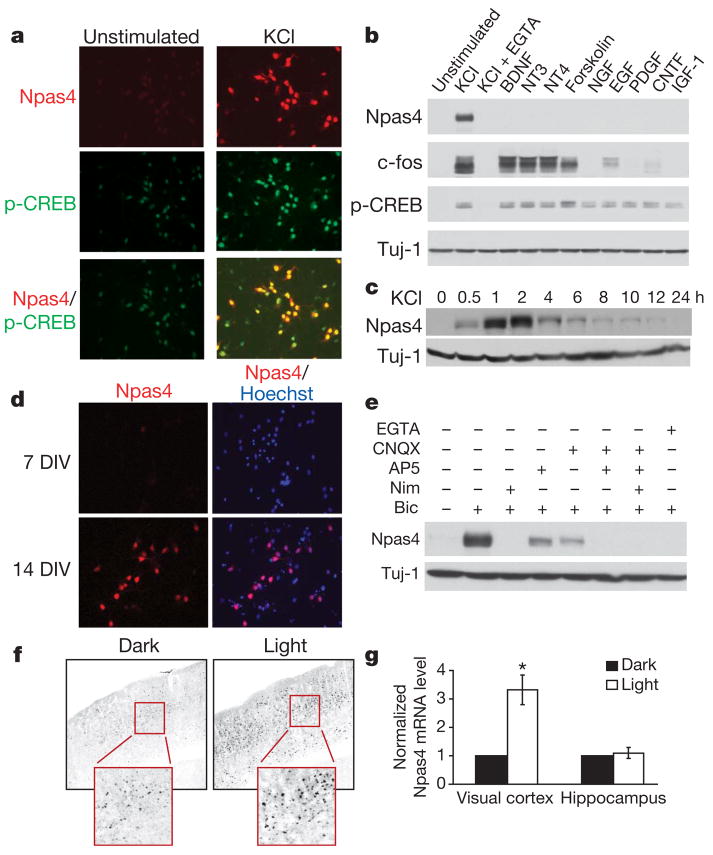
Figure 1. Npas4 expression is regulated by neuronal activity in vitro and in vivo.
a, Immunostaining showing Npas4 protein is induced in rat hippocampal neurons (7 DIV) by depolarization (50 mM KCl, 2 h, right). p-CREB, CREB phosphorylated at Ser 133. b, Western blot showing Npas4 is selectively induced by membrane depolarization (50 mM KCl, 7 DIV rat hippocampal neurons), but not by BDNF (50 ng ml−1), NT3 (50 ng ml−1), NT4 (50 ng ml−1), forskolin (10 μM), NGF (100 ng ml−1), EGF (100 ng ml−1), PDGF (100 ng ml−1), CNTF (100 ng ml−1) or IGF-1 (100 ng ml−1). Induction is prevented by pretreatment with the Ca2+ chelator EGTA (5 mM, 10 min). c, Western blot showing Npas4 (7 DIV rat hippocampal neurons) is transiently induced by membrane depolarization (50 mM KCl, 30 min). d, Basal Npas4 expression increases as neurons mature, presumably because of increased endogenous spontaneous activity: compare immunostaining of 7 and 14 DIV rat hippocampal neurons. e, Western blot showing stimulation of primary hippocampal neurons (14 DIV) with bicuculline (50 μM, 2 h) increases Npas4 expression levels. This is prevented by pretreatment with nimodipine (5 μM, 1 h) or EGTA (5 μM, 5 min) and reduced by pretreatment (1 h) with antagonists to NMDA receptors (100 μM AP5) or AMPA receptors (50 μM CNQX). f, g, Mice dark-reared for one week (P21–P28) and then stimulated with strobe lights have greater Npas4 expression levels in the visual cortex than their dark-reared littermates, but there is no difference in the hippocampus. Light stimulation was applied for 2 h for immunocytochemistry analysis (f) or 1 h for Npas4 mRNA quantification (g). Significance was determined using a one-tailed paired t-test, *P < 0.05. Data are shown as mean ± s.e.m.