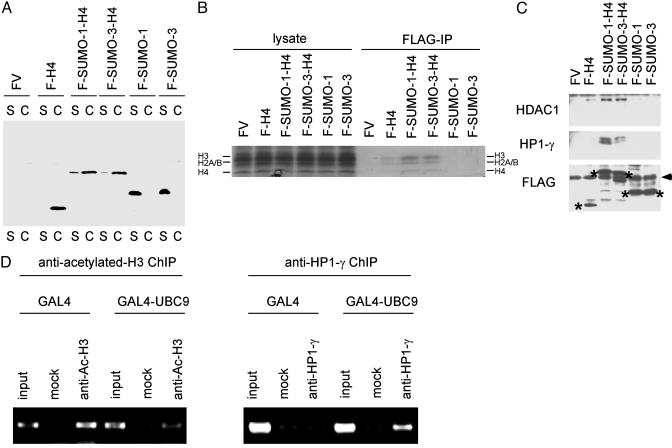
Fig. 5.
Histone sumoylation is associated with recruitment of HDAC and HP1. (A) Incorporation of SUMO-H4 fusion proteins into chromatin. The 293 cells were transfected with FLAG-vector (FV), FLAG-H4, FLAG-SUMO-1-H4, FLAG-SUMO-3-H4, FLAG-SUMO-1, or FLAG-SUMO-3, and the cells were fractionated into soluble (S) and chromatin (C) fractions as described (26). The location of each FLAG-tagged protein was determined by anti-FLAG immunoblotting. (B) Association of SUMO-H4 fusion proteins with core histones. The 293 cells were transfected with FLAG vector, FLAG-H4, FLAG-SUMO-1-H4, FLAG-SUMO-3-H4, FLAG-SUMO-1, or FLAG-SUMO-3, and 2 days later cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG Ab under nondenaturing conditions. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and Coomassie staining for the presence of core histones (H4, H2A/B, and H3). (C) Interaction of SUMO-H4 fusion proteins with HDAC1 and HP1-γ. The 293 cells were transfected with FLAG vector, FLAG-H4, FLAG-SUMO-1-H4, FLAG-SUMO-3-H4, FLAG-SUMO-1, or FLAG-SUMO-3, and 2 days later cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG Ab (under native conditions) and analyzed by anti-HDAC1 (Top) or anti-HP1-γ (Middle) immunoblotting. The expression level of each FLAG-tagged protein (shown by *) was examined by anti-FLAG immunoblotting (Bottom). The position of Ig light chain is shown by the arrowhead (Bottom). (D) Histone deacetylation and recruitment of HP1-γ induced by GAL4-UBC9. HeLa cells were cotransfected with 4XGAL14D luciferase reporter and GAL4 or GAL4-UBC9. Two days later, histone acetylation status and recruitment of HP1-γ near the GAL4 sites were examined by antiacetylated histone H3 (Left) and anti-HP1-γ (Right) chromatin immunoprecipitation under nondenaturing conditions.