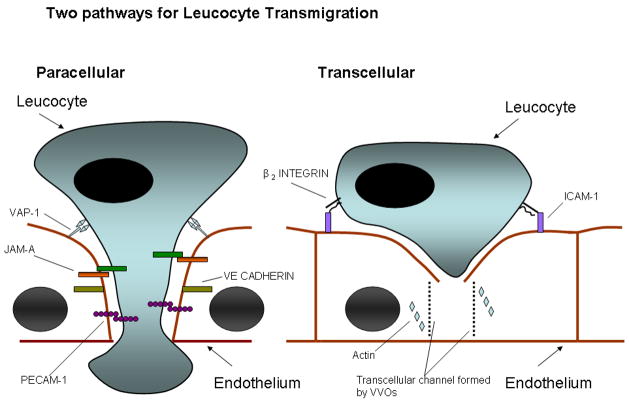
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of two pathways that may be taken by leucocytes during transmigration across endothelial layers. The paracellular route involves loosening of endothelial tight junctions (maintained by VE-cadherin) and migration of the leucocyte through the junction by binding to adhesion molecules ( PECAM-1 and JAM-A). In the context of the liver we believe that VAP-1 also plays a significant role in this process. The transcellular route involves interaction with ICAM-1 on the endothelial surface which leads to a channel forming through the endothelial cell by the formation of VVOs (vesiculo-vacuolar organelles). This channel is supported by cytoskeletal proteins such as actin.