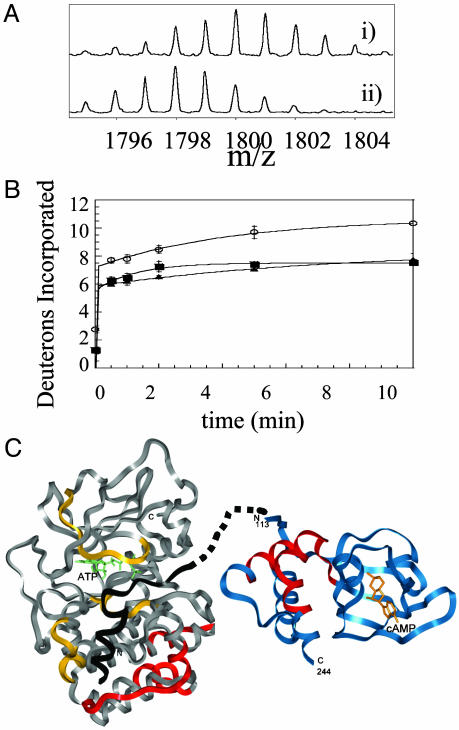
Fig. 2.
(A) Expansion of the MALDI-TOF mass spectra to show one of the 17 fragments (m/z = 1,793.97, residues 247–261) from the analysis of the C-subunit that experienced slowed exchange in the RIα2–C2 holoenzyme complex. (Ai) The isotopic envelope for the fragment from the free C-subunit bound to MgATP after 10 min of deuteration. (Aii) The isotopic envelope for the same fragment from the RIα2–C2 holoenzyme after 10 min of deuteration. (B) Plot of deuterium incorporation into the amide positions of the region of C-subunit for the peptide fragment; m/z = 1,793.97 from C-subunit +MgATP (○), RIα2–C2 holoenzyme (▪), and RIα(94–244)-C holoenzyme (▴). (C) The structure of the C-subunit is shown in gray; the residues protected by the R-subunit are shown in red; the inhibitor peptide PKI(5–24), which mimics the pseudosubstrate, is shown in black; and the residues protected by it are shown in yellow (8). The structure of RIα(113–244) is shown in blue with the residues protected by the C-subunit in red. The pseudosubstrate/inhibitor sequence is shown connected by dots to the N terminus of the structured part of RIα.