Figure 5.
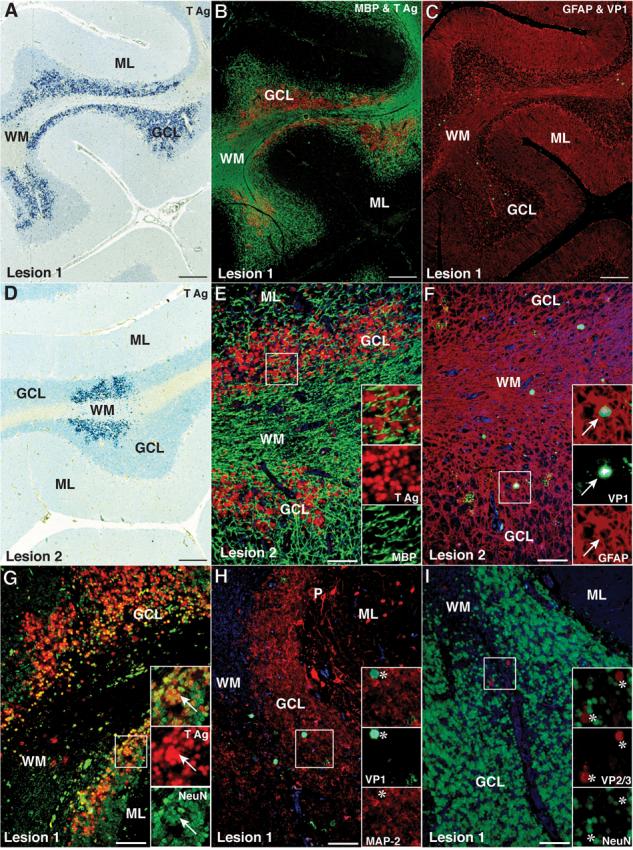
Numerous JCV-infected GCNs expressing T Ag are present in the cerebellum of an HIV-positive control patient without PML. (A, D) Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining for T Ag (v-300, blue) with hematoxylin counterstaining showing 2 areas of the cerebellum containing numerous T Ag- expressing cells in the granule cell layer (GCL) and a few in the white matter (WM) (bar = 250 μm). (B, E) Double IFA staining for oligodendrocytes and myelin (MBP, SMI-94, Alexa Fluor 488, green) and T Ag (v-300, Alexa 568, red) reveals preservation of the myelin in the WM (B, bar = 250 μm). A higher magnification view (E, bar = 50 μm) reveals no T Ag+/MBP+ oligodendrocytes in the GCL (inset, and separate red and green channels). (C, F) Double IFA staining for astrocytes (rabbit polyclonal anti-GFAP, Z0334, Alexa Fluor 568, red) and VP1 capsid protein (PAB597, Alexa Fluor 488, green) shows that the rare cells expressing VP1 (C, bar = 250 μm) are GFAP+ astrocytes (F, bar = 50 μm) located in WM or at the WM-GCL junction (inset, arrow, and separate green and red channels). (G) Double IFA with the neuronal marker mouse monoclonal anti-NeuN (Alexa Fluor 488, green) and the T Ag (v-300, Alexa Fluor 568, red) shows that most of the numerous JCV-infected cells in the GCL are T Ag+/NeuN+ GCNs (inset, yellow, arrows) (bar = 50 μm). (H) Double IFA for the neuronal marker mouse monoclonal anti-MAP-2 (HM-2, Alexa Fluor 488, green) and the rabbit polyclonal anti-VP1 capsid protein (ab53977, Alexa Fluor 568, red) show only MAP-2−/VP1+ glial cells in the GCL (asterisk, insets) and no VP1-expressing GCNs (bar = 50 μm). (I) Double IFA with the neuronal marker mouse monoclonal anti-NeuN (A60, Alexa Fluor 488, green) and the rabbit polyclonal anti-VP2 and VP3 (VP2-3) capsid proteins (ab53983, Alexa Fluor 568, red) reveals only NeuN−/VP2-3+ glial cells in the GCL (asterisk, insets) and no GCNs expressing VP2 or VP3 (bar = 50 μm). (ML, molecular layer).
