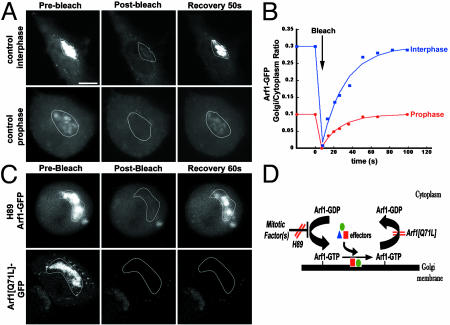
Fig. 4.
Arf1 dynamics in untreated, H89-treated, and Arf1[Q71L]-expressing cells. (A) Photobleaching the Golgi pool of Arf1-GFP in interphase and prophase cells and monitoring recovery of fluorescence. (B) An example of recoveries observed for one interphase cell and one prophase cell. The Golgi to cytoplasm ratio of Arf1-GFP was plotted through the course of the experiment. (C) Photobleaching the Golgi pool of Arf1-GFP in an H89-treated metaphase cell or an Arf1[Q71L]-GFP-expressing cell. In H89-treated cells, Arf1-GFP recovered rapidly upon photobleaching the Golgi pool of its fluorescence (Upper), whereas Arf1[Q71L]-GFP-expressing cells showed negligible recovery over the same time period (Lower). (D) Model for Arf1 inactivation during mitosis and the effects of H89 and Arf1[Q71L]. Recruitment of Arf1 to Golgi membranes is inhibited early in mitosis by a mechanism that is sensitive to H89. This leads to the accumulation of Arf1-GDP in the cytoplasm, the inability to recruit Arf1 effector proteins onto Golgi membranes, and the disassembly of the Golgi. These mitotic effects can be inhibited either by expression of Arf1[Q71L] or by H89 treatment. (Bar, 10 μm.)