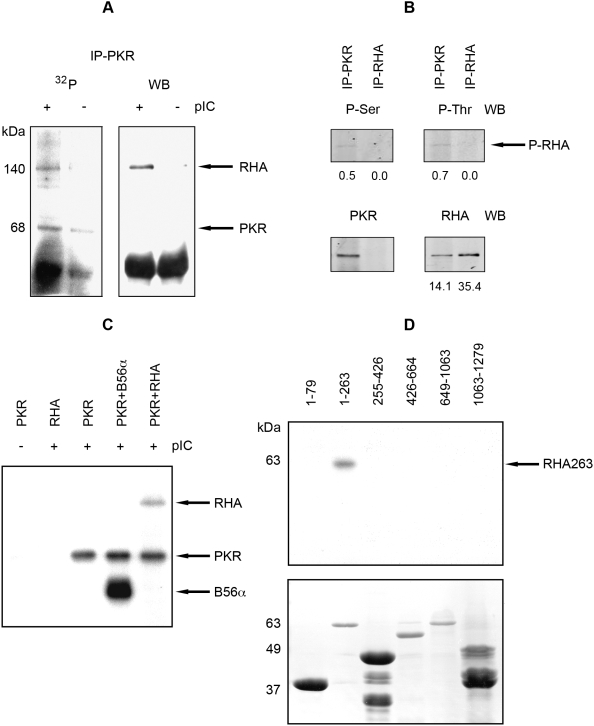
Figure 3. RHA is a substrate for PKR.
(A) An autoradiograph (32P; on the left) and Western blot (WB; on the right) showing electrophoretically separated proteins labeled with 32P by PKR in a kinase assay, or probed with a rabbit anti-RHA antibody, respectively. Proteins were immunoprecipitated with mouse anti-PKR (IP-PKR) from MEFs expressing human PKR either untreated (−) or treated (+) with pIC. (B) A Western blot showing electrophoretically separated proteins immunoprecipitated from HeLa cells with anti-PKR (IP-PKR) or anti-RHA (IP-RHA) antibodies, then probed with anti-phosphoserine (P-Ser) and anti-phosphothreonine (P-Thr). Arrows indicate phosphorylated RHA (P-RHA). Blots were stripped and re-probed with anti-RHA, or anti-PKR antibodies. Primary antibodies were detected using fluorescent-labeled secondary antibodies. The intensity of the immune-positive bands from the blot was quantitated, and these values are given at the bottom of each panel as relative arbitrary units. (C) An autoradiograph of electrophoretically separated proteins labeled with 32P by PKR in an in vitro kinase assay. Arrows indicate autophosphorylated PKR and phosphorylated RHA, and, as a control, the previously established PKR substrate B56α. PKR activity is induced by treatment with pIC, indicated at the top of the figure (−/+). (D) An autoradiograph of GSTRHA peptides 32P-labeled by PKR in a kinase assay and electrophoretically separated by SDS-PAGE gel (upper panel). Amino acid end points for each RHA construct are indicated over each lane. The arrow indicates the phosphorylated RHA peptide (RHA263). The lower panel shows the Coomassie-stained, SDS-PAGE gel assayed above.