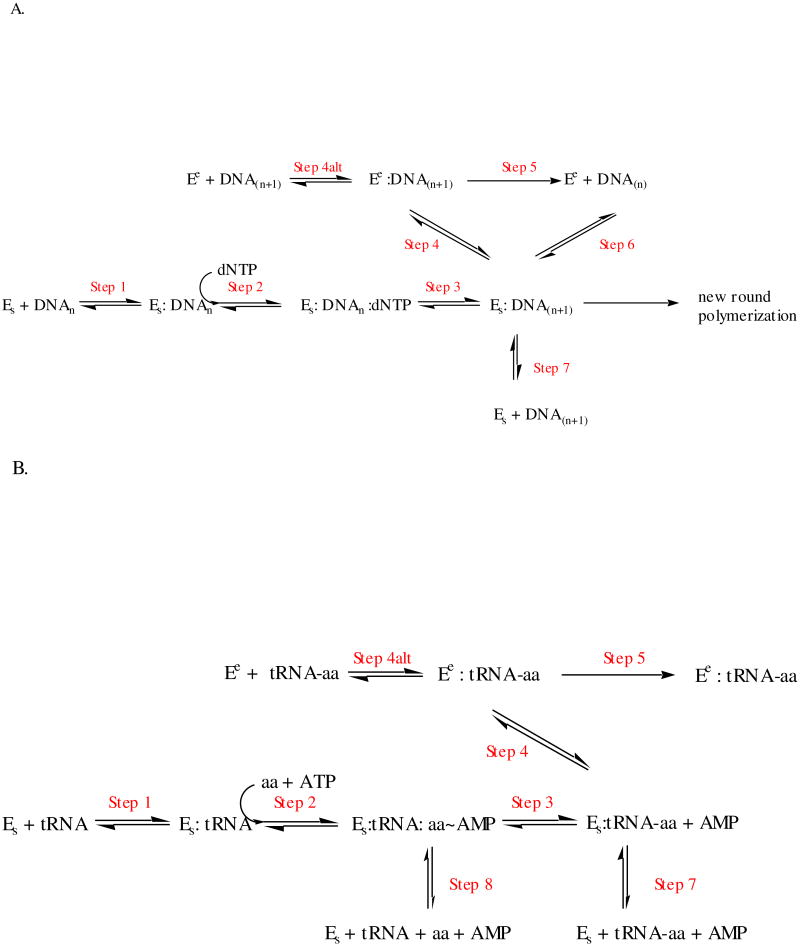
Figure 2.
Idealized kinetic schemes for synthesis and editing by replicative DNA polymerases (A) and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (B). In both schemes, Es refers to the enzyme with substrates bound in the synthetic site, and Ee refers to enzyme with substrates bound in the editing site. E in panel A refers to the DNA polymerase, while E in panel B refers to the ARS. Step 2 in panel A (polymerases) refers only to the binding step for the incoming dNTP, while Step 2 in panel B (ARSs) include both the amino acid and ATP binding step and adenylation reaction. The merging of the binding and adenylation chemistry step for the ARSs is depicted in this fashion to simplify the global comparison between the two families. Additional elementary steps that may follow the binding of substrates and precede chemistry have been omitted by clarity. These include domain closure and other conformational changes, which may be rate limiting in some systems. In Panel A, the translocation of the primer-template from the editing site to the synthetic site (Step 6) is shown for aesthetic reasons to be in equilibrium with the species Es:DNA(n+1), but this is formally incorrect. Technically, the true species is Es:DNA(n), which is the immediate product of Step 1.