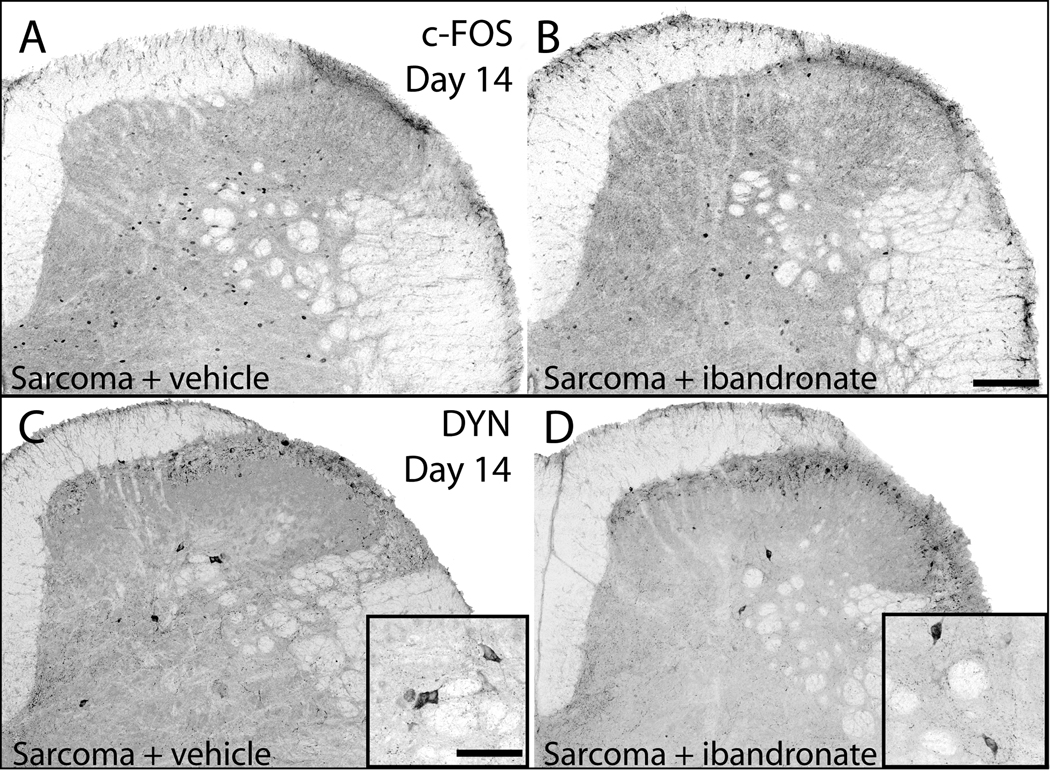
Figure 4.
Neurochemical changes associated with central sensitization are attenuated by administration of ibandronate. Representative confocal images of c-Fos expressing neurons of the spinal cord in sarcoma + vehicle (A) and sarcoma + ibandronate (B) mice. Following a normally non-noxious palpation of tumor-bearing limbs, sarcoma + vehicle mice showed an increased expression of c-Fos protein in neurons within the deep laminae. In sarcoma animals that received ibandronate therapy, there was a significant reduction of this increased expression of c-Fos protein. Representative confocal images of prodynorphin expression (DYN) in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord in sarcoma + vehicle (C) and sarcoma + ibandronate (D) mice. Sarcoma + vehicle mice displayed an increase in prodynorphin-IR neurons in deep laminae of the ipsilateral spinal cord (C), whereas ibandronate therapy significantly attenuated the increase in prodynorphin expression (D). Scale bar: A, B 150mcm; insets in C,D 200mcm.