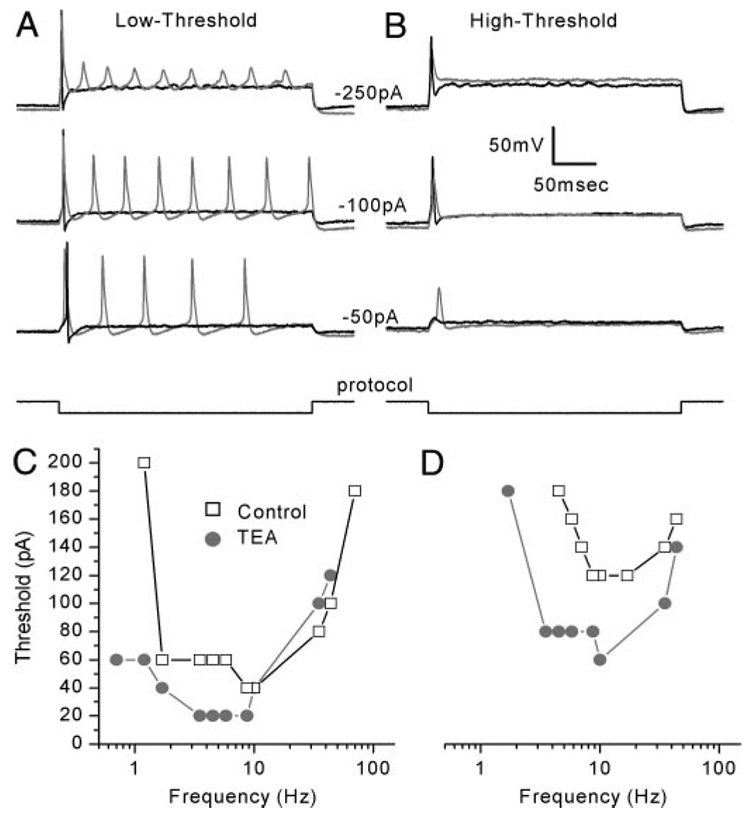
FIG. 9. TEA lowered the threshold of low- and high-threshold neurons and shifted their sensitive ranges to lower frequencies.
A: TEA application lowered the threshold for action potential firing, induced multiple action potentials, and increased AP width in a representative low-threshold neuron (control: black, TEA: gray, Cell 20030624A, P2). B: TEA lowered the threshold for action potential generation and broadened the width of the spike in a representative high-threshold neuron (control: black, TEA: gray, Cell 20030715A, P1). C and D: tuning curves for low- (C) and high- (D) threshold neurons. In the presence of TEA, both neurons had a lower threshold and fired action potentials at lower frequencies relative to controls (Low-threshold: Cell 20030702D, P2; high-threshold: Cell 20030709C, P3).