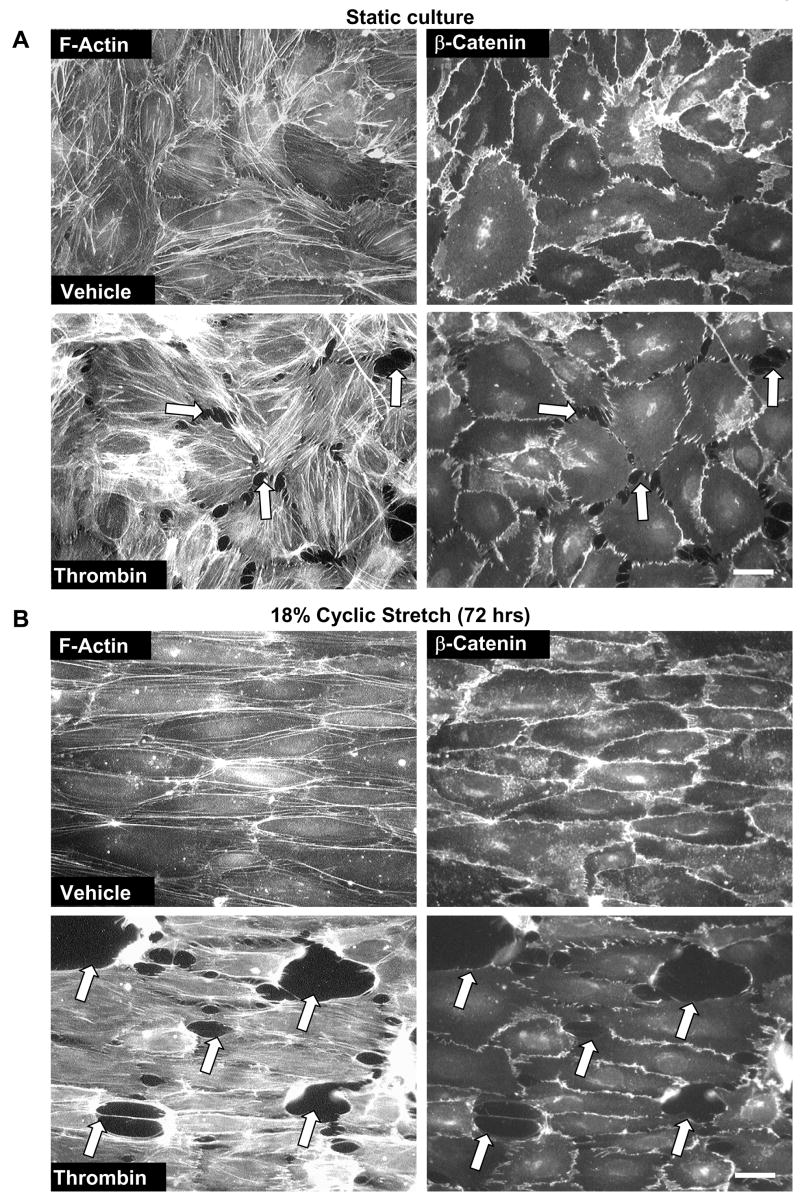
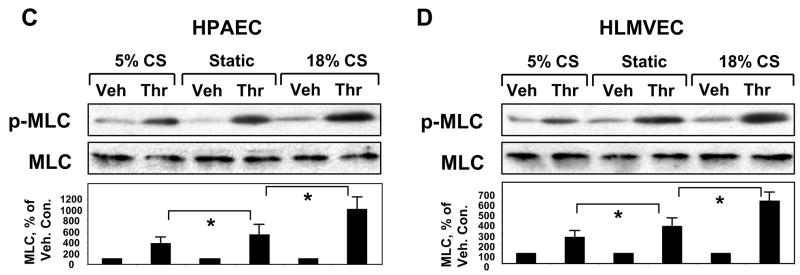
Figure 2. Effects of long term CS on thrombin-induced cytoskeletal and adherens junction remodeling and paracellular gap formation.
Pulmonary EC grown to confluence on BioFlex plates were left under static conditions (A) or exposed to pathologic 18% CS for 72 hrs (B) followed by stimulation with thrombin (0.1 U/ml, 10 min). Immunofluorescence double staining was performed using Texas-Red phalloidin to detect F-actin and β-catenin to detect adherens junctions. Paracellular gaps are marked by arrows. Results are representative of three independent experiments. Scale bar = 10 μm. HPAEC (C) or HLMVEC (D) were subjected to 5% or 18% CS for 72 hrs or left static. Phosphorylated MLC was detected by immunoblotting with di-phospho-MLC specific antibodies. Quantitative analysis depicts relative levels of phosphorylated target proteins expressed as ratio of phospho-protein to the total protein in the same lysate. In some experiments, the levels of phosphorylated and total target proteins were detected by immunoblotting of two or more identically loaded membranes with corresponding antibody. Results are representative of three independent experiments.