Fig. 4.
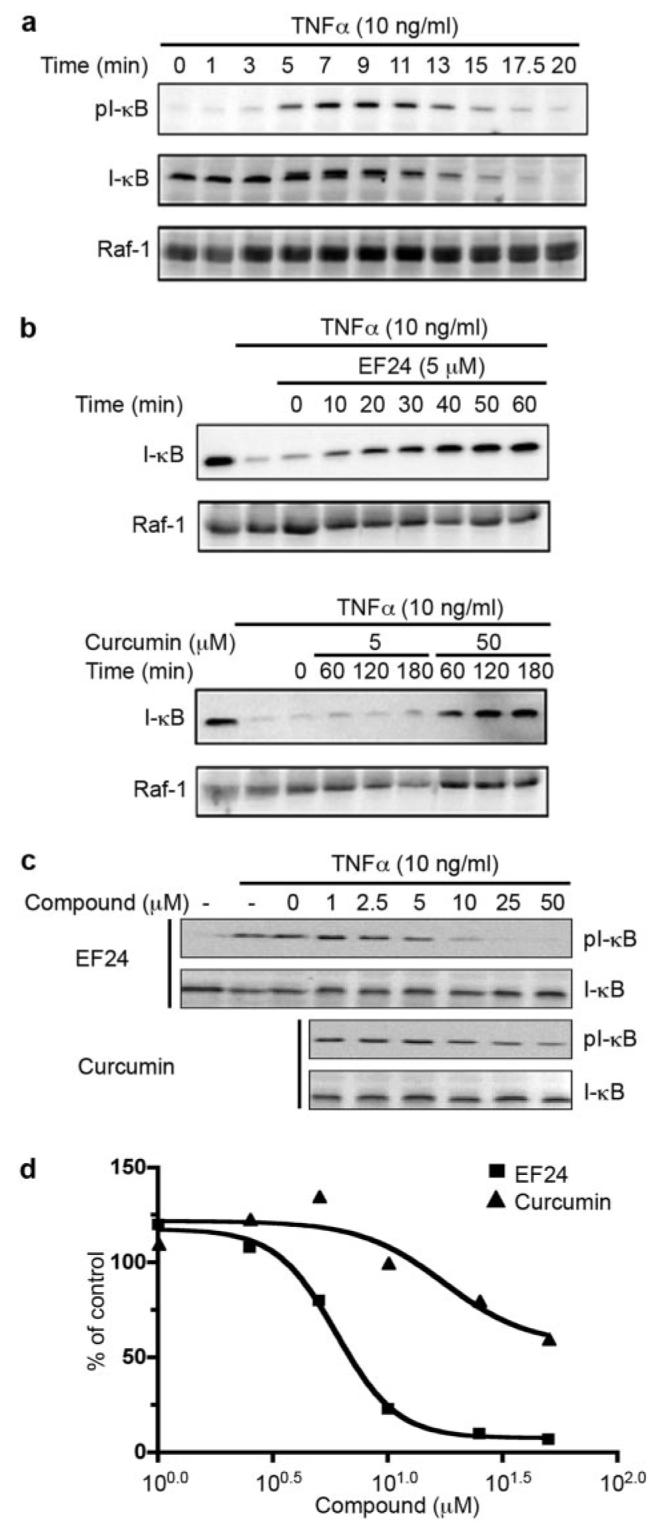
EF24 blocks TNF-α-induced IκB degradation and phosphorylation. a, A549 cells were treated with 10 ng/ml TNF-α. Whole cell lysates were prepared at indicated times and analyzed for the phosphorylation state of IκB with anti-pS32 antibody via Western blotting (top). Then, antibodies on the membrane were stripped and the membrane reprobed for total IκB with antiserum against IκB (middle). Raf-1 was used as a control (bottom). b, A549 cells were pretreated for various times with 5 μM EF24, or 5 or 50 μM curcumin before the addition of TNF-α. Cells were cultured in the presence of 10 ng/ml TNF-α for an additional 20 min, lysed, and analyzed for total IκB levels by Western blot (top). Raf-1 was used as a control (bottom). c, A549 cells were pretreated with compounds (EF24 or curcumin) as indicated for 30 min. TNF-α was added to induce IκB phosphorylation. Cell lysates were prepared after 7 min of treatment and used for probing pS32-IκB followed by probing total IκB with Western blots. Intensity of cross-reacting material bands on Western blots was estimated with a Kodak imaging system. The phosphorylation levels of IκB at S32 are normalized to total IκB and expressed relative to control sample with DMSO treatment (d).
