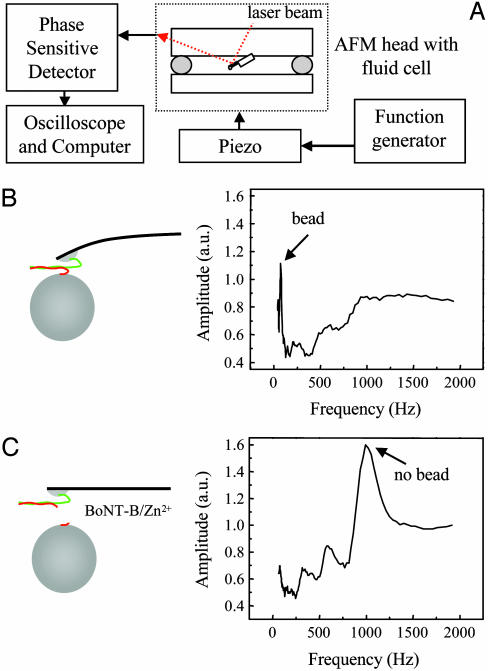
Fig. 3.
(A) Schematic representation of the experimental setup used for the BoNT-B sensor. The syntaxin 1A-functionalized cantilevers with attached synaptobrevin 2-functionalized beads residing in the fluid cell of the AFM head were acoustically vibrated by means of a piezo driven by a function generator. The vibration amplitude of the cantilever was monitored by using the difference signal from a split photodiode system that collects the red laser beam reflected off the back of the cantilever. A phase-sensitive detector was used to measure the vibration amplitude as a function of the frequency, and the data were recorded in a digital oscilloscope and later exported to a computer. (B) A typical amplitude spectrum (Right) obtained for the cantilever with the bead attached (Left). The lowest-order resonance attributable to the combined cantilever-bead system is indicated by the arrow. (C) Three minutes after the injection of solution containing BoNT-B and zinc ions (BoNT-B/Zn2+; 42 nM/104 μM) into the fluid cell, the sharp cantilever-bead resonance disappears, while the bare (no bead) cantilever resonance peak appears (Right, arrow), indicating the detachment of the bead from the cantilever. The vibration amplitude is expressed in arbitrary units (a.u.). Drawings are not to scale.