Figure 2.
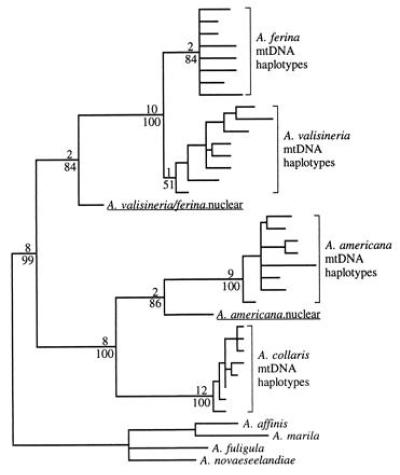
Strict consensus of 1248 shortest trees (288 steps) for mtDNA control region sequences and homologous nuclear sequences found in parsimony analysis assuming equal weights for all character state changes. Branch lengths are proportional to the number of steps along each branch with acctran optimization. Alignment gaps were introduced in one or more taxa at 22 of 392 positions. We excluded positions 1–65 and 366–392 due to missing data in some taxa. The same set of shortest trees was found in all 100 random addition sequence replicates. Decay indices (number of additional steps required in a tree without the node in question) and bootstrap percentages are given above and below branches, respectively. Eight mtDNA haplotypes representing the range of observed variation were selected for A. ferina, A. valisineria, A. americana, and A. collaris. mtDNA haplotypes of A. affinis, Aythya marila, Aythya fuligula, and Aythya novaeseelandiae were designated as the outgroup. These eight species form a clade with no other extant members (see Fig. 3). Because of computational limitations, bootstrap percentages and decay indices were obtained using a smaller data set that included only four mtDNA haplotypes of each of the ingroup taxa.
