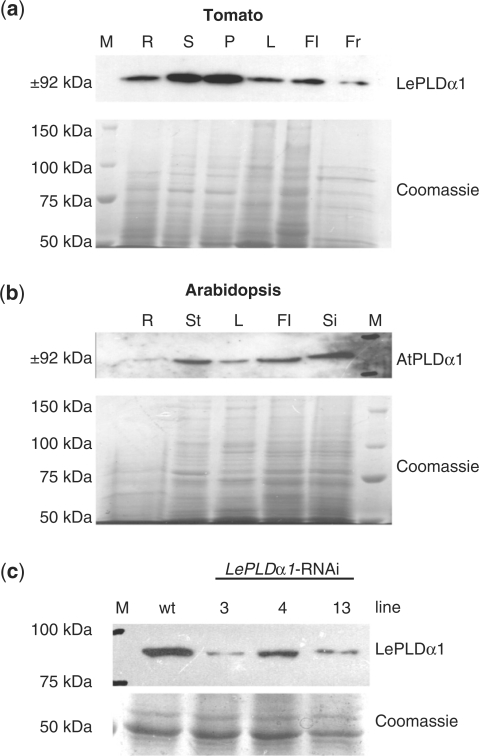
Fig. 3.
Silencing LePLDα1 in tomato plants. (a) Proteins were extracted from roots (R), stems (S), petioles (P), leaves (L), flowers (Fl) and fruit (Fr) harvested from mature tomato plants. Proteins were separated by SDS–PAGE and blotted or stained with Coomassie brilliant blue as a loading control. A precision protein marker (M) was used to gauge the size of the detected band. (b) Protein blot analysis of AtPLDα1 protein levels was performed on proteins extracted from roots (R), inflorescence stems (St), leaves (L), flowers (Fl) and siliques (Si) of flowering Arabidopsis plants. (c) Protein blot analysis of LePLDα1 protein levels was performed on proteins extracted from 1-week-old wild-type (wt) and LePLDα1-silenced tomato seedlings.