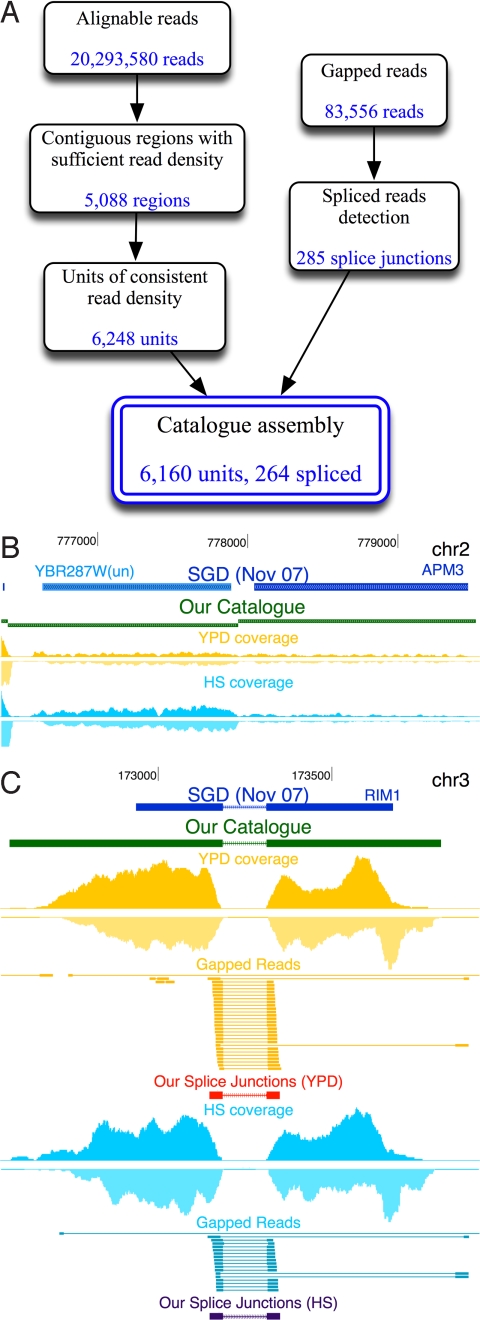
Fig. 2.
Ab initio assembly of a transcript catalog. (A) Outline of steps in the catalog construction pipeline. (B) Segmentation of a contiguously transcribed region into 2 regions of distinct expression levels corresponding to the genes YBR287W and APM3. When using YPD reads alone, both genes exhibit similar coverage and thus cannot be segmented. However, in HS, they are differentially expressed, and hence by combining observations from both conditions the automatic segmentation procedure (see Materials and Methods) correctly separates them to 2 units. Tracks from top to bottom: SGD annotations (blue), our catalog (green), read coverage at YPD (yellow), and read coverage at HS (blue). (C) Detection of splice junctions. Full and gapped reads mapped to the RIM1 genomic locus. Tracks are as in B, together with gapped reads (connected segments), our putative splice junctions (in red and blue), including the junction orientations as estimated by donor and acceptor sequence motifs (arrows). As shown, our procedure identifies the exact coordinates and orientation of the known splice site.